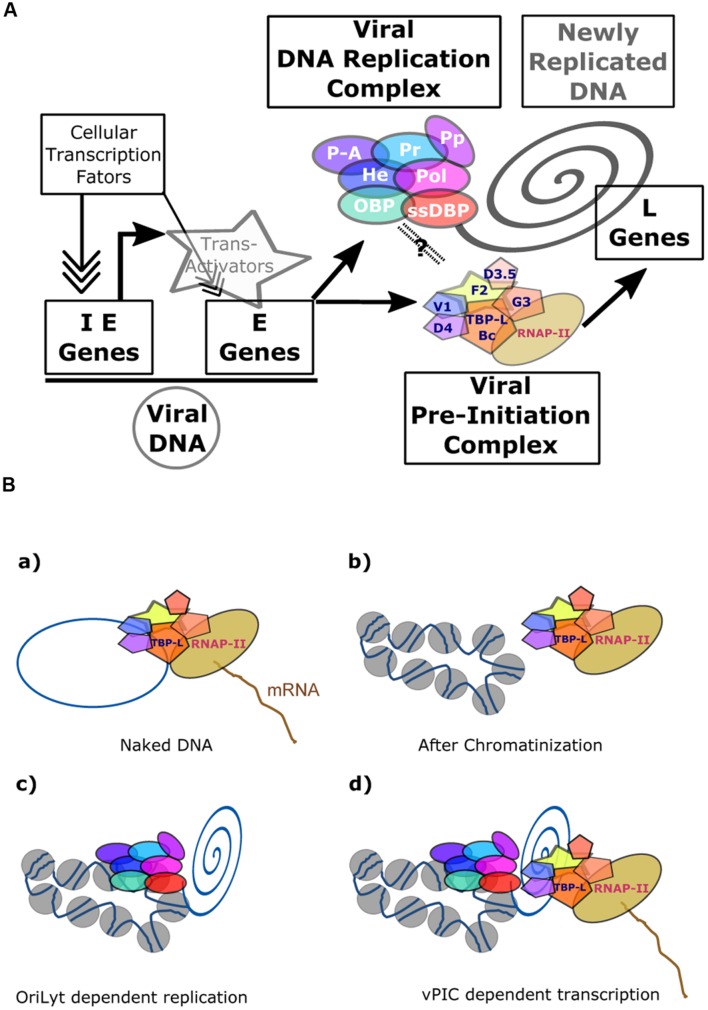
FIGURE 5.
Transcriptional regulation of β- and γ-herpesviruses late gene expression. (A) Overview of EBV productive cycle. The viral immediate-early and early genes are transcribed from the episomic viral DNA and their expression controlled by the cellular transcription machinery formed around the cellular PIC. Expression of the late viral genes is dependent upon viral DNA replication and on the presence of the viral specific Pre-Initiation Complex (vPIC) composed of five viral proteins associated with the viral TATT-box binding protein like (TBP-L). (B) Expression of the late viral genes is linked to newly replicated DNA. vPIC alone can activate the expression of a late gene present on a plasmid during a transient transfection assay (a), but it is not able to induce the expression of a late viral gene present on a stable episome (b). The chromatinized DNA bearing the OriLyt origin of DNA replication can be replicated by the viral DNA replication complex (c). In these conditions, vPIC, present in the replication factories, can activate expression of the late viral genes (d). The link between the replication complex and vPIC is not proven but several arguments described in the main text strongly argue in favor of such a model. IE, immediate-early; E, early; L, late; OBP, origin-binding protein; He, helicase; Pol, polymerase; ssDBP, single-strand DNA-binding protein; Pr, primase: P-A, primase associated: PP, Polymerase processivity; TBP-L, TATA-binding protein like; Bc, BcRF1; F2, BFRF2; G3, BGLF3; V1, BVLF1; D4, BDLF4; D3.5, BDLF3.5.