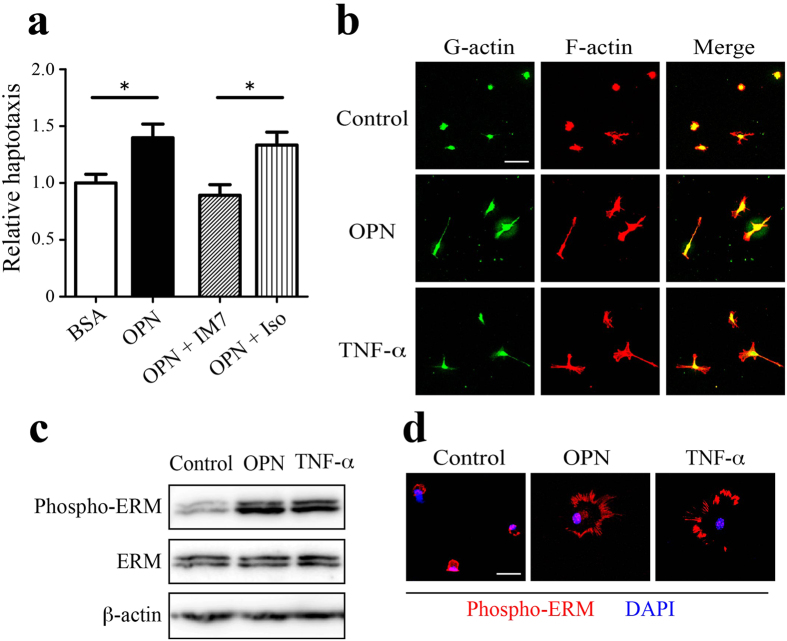
Figure 7. OPN induces CD44-mediated migration and morphological changes in cultured astrocytes.
(a) Astrocyte haptotaxis toward OPN was mediated by CD44. The lower surface of migration chamber filters was coated with BSA (control) or OPN. Cultured astrocytes were added to the upper side of the migration chamber filters, and cells that migrated to the lower side were counted. Astrocyte haptotaxis toward OPN was inhibited by an anti-CD44 neutralizing antibody (IM7) but not by an isotype control antibody (Iso). Each bar represents the mean ± SEM relative to the mean of BSA-coated filters (n = 13–14). *p < 0.05, two-tailed Student’s test. (b) OPN induces morphological changes in cultured astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were cultured for 24 h in the absence (Control) or presence of OPN (1 μg/mL) or TNF-α (50 ng/mL), and labeled with DNase I (green) or phalloidin (red) to visualize G-actin and F-actin, respectively. Cell hypertrophy with extension of filopodia was evident in the OPN- or TNF-α-treated astrocytes. (c, d) OPN induces ERM activation. Primary astrocytes were treated with OPN or TNF-α as described above. Western blot analysis using an anti-phospho-ERM antibody revealed enhanced phosphorylation of ERM by OPN or TNF-α. Full-length gels are shown in Supplementary Fig. 10c. Representative blot of out of three experiments. Fluorescent phospho-ERM signals (red) were detected in filopodia-like leading edges of astrocytes treated with OPN or TNF-α. Scale bar, 50 μm (b); 20 μm (d).