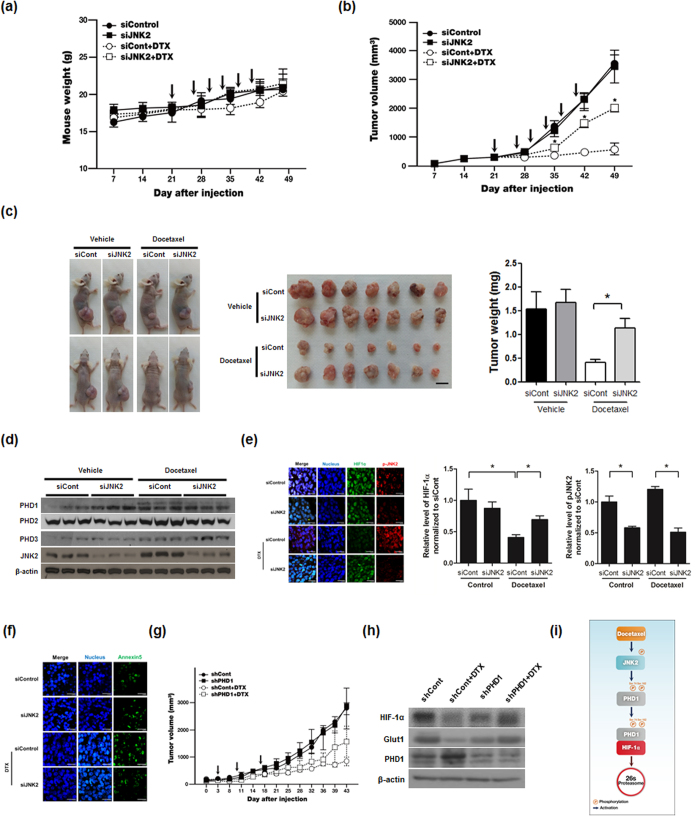
Figure 6. Docetaxel-induced activation of the JNK2/PHD1 signaling pathway induces HIF-1α degradation and cancer cell death in a mouse xenograft model.
(a) Effect of docetaxel (DTX) on body weight during the course of the experiment. Arrows indicate treatment of DTX. (b) Effect of docetaxel-induced activation of the JNK2/PHD1 signaling pathway on tumor growth. Arrows indicate treatment of DTX. (c) Left panel: Representative images captured 7 week post-inoculation; middle panel: Images of individual MDA-MB-231 tumors at the time of sacrifice; right panel: Average tumor weight at sacrifice. (n = 7 animals/group; P < 0.05, unpaired t-test). (d) After mice were sacrificed, tumors were lysed and PHD1, PHD2, PHD3, JNK2, and β–actin were detected by immunoblot analysis. (e) Left panel: Immunofluorescence staining of HIF-1α and JNK2 in paraffin-embedded tissue specimens from mouse xenograft tumors. Middle panel: Signal intensities of HIF-1α were quantified using Image J. Right panel: Signal intensities of pJNK2 were quantified using Image J. (f) Apoptosis in tumor sections of the indicated experimental groups were determined using an in situ cell death detection kit. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 7; *P < 0.05, unpaired t-test). (g) MDA-MB-231/pshCont (shCont) and MDA-MB-231/pshPHD1 (shPHD1) cells (5 × 105) were injected subcutaneously into the right flank of BALB/c nude mice. Once tumors had become established, they were treated with docetaxel (7.5 mg/kg/injection) weekly for 3 weeks. Tumor growth was assessed by calculating tumor volume using the following formula: Tumor volume = length × (width)2 × 0.5 (n = 3 animals/group; P < 0.05, unpaired t-test). Arrows indicate treatment of DTX. (h) After mice were sacrificed, tumors were lysed and PHD1, HIF-1α, GLUT1 and β–actin were detected by immunoblot analysis. (i) Schematic model showing how docetaxel induces cancer cell death under hypoxic conditions through JNK2/PHD1 signaling-mediated HIF-1α degradation.