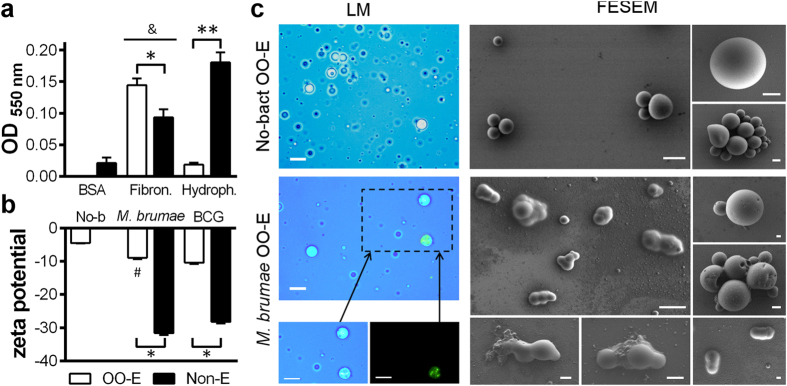
Figure 6. Characterization of OO-M. brumae emulsion.
(a) Adhesion of M. brumae to BSA-coated (control), fibronectin-coated and uncoated (hydrophobicity assay) polystyrene plates. The bars represent means ± SEMs of absorbance values of triplicate wells from three independent experiments. &p < 0.05 versus respective BSA-coated wells; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001 (Mann-Whitney U test). (b) Zeta potential of mycobacteria preparations. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of 20 measurements of each triplicate sample from two independent experiments. #p < 0.01 versus OO-E BCG; *p < 0.001 versus Non-E (Mann-Whitney U test). (c) Light microscopy (LM): trypan blue and fluorescence staining in upper images and separated canals in bottom images, and Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) images of OO emulsions with (M. brumae OO-E) or without (No-bact OO-E) M. brumae. Bars: 10 μm in images of LM; in FESEM: 5 μm, in the general views (2 large images), and 1 μm, in images of the details. OO, olive oil; Non-E, mycobacteria in PBS-tween; No-b, No-bact, preparation without bacteria; BSA, Bovine Serum Albumina; Fibron, fibronectin; Hydrofob, Hydrofobicity assay.