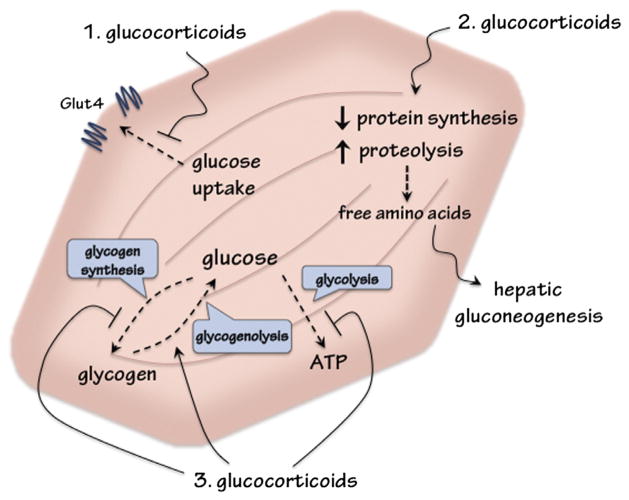
Fig. 1.
Metabolic influences of glucocorticoids (GCs) in skeletal muscle to regulate glucose homeostasis. (1) GCs inhibit insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. (2) GCs decrease protein synthesis and increase proteolysis to release amino acids for hepatic gluconeogensis. (3) GCs downregulate glucose utilization by inhibiting glycolysis. GCs also suppress glycogen synthesis, and act with catecholamine to upregulate glycogenolysis.