Fig. 6. Cell invasion – Colorimetric maps.
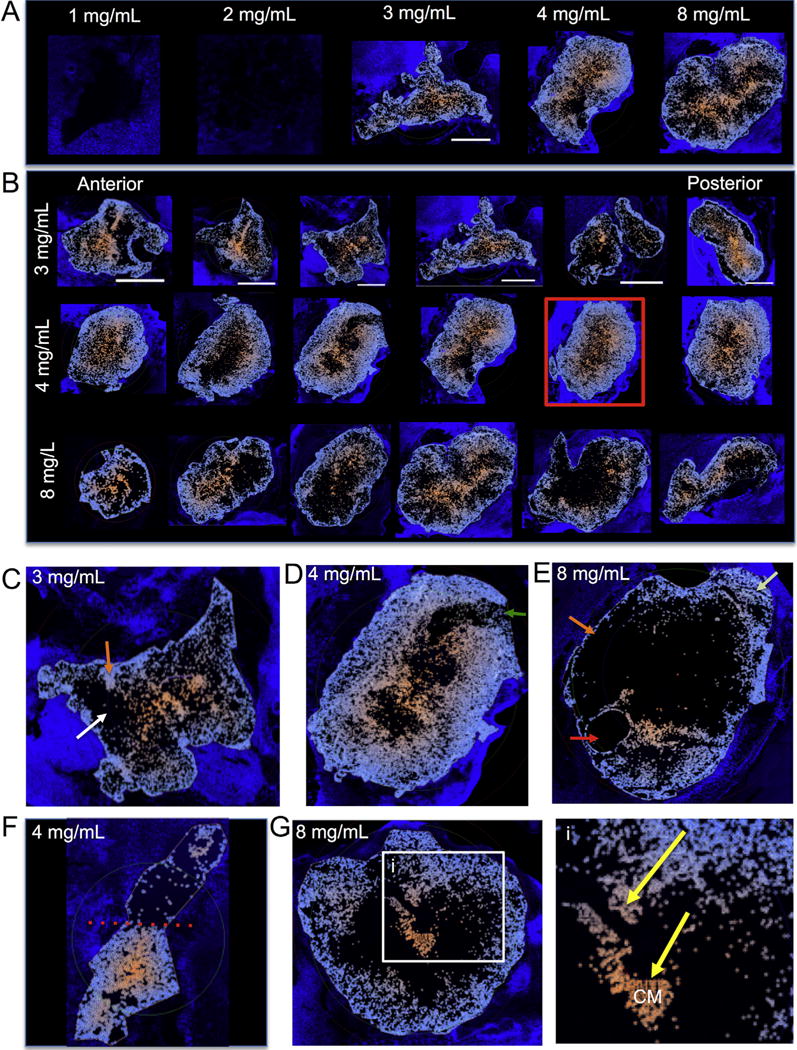
Identification and labeling of cell invasion at different concentrations using Lux64R based on DAPI staining within a collagen I outline ROI. Using a colorimetric method ranging from light blue (closest to the host boundary) to orange (furthest from host boundary), maps of cell invasion were created to highlight differences between ECM concentrations (A). These maps also allowed us to inspect the anterior-posterior invasion of cells within the ECM hydrogel. It was evident here that the smaller ECM hydrogel areas found at the poles of the cavity saw a more complete coverage of cell invasion compared to more central slices which occupied a large area (B). Invasion typically followed a concentric pattern that saw cells migrating to the center of mass of the injected ECM hydrogel, in some cases leading to very homogenous distribution of host cells through the material (red box). Nevertheless, important qualitative differences in cell invasion were also noted on these colorimetric maps. Cell invasion in some instance followed a very densely packed channel with blind spots within the material hardly seeing any invasion (C). In other cases, there was a no significant invasion (green arrow) in a very restricted region suggesting that potential host factors, such as scarring can influence invasion (D). Indeed, the varied pattern of invasion or the lack therefore indicates that technical factors, such as an air bubble (red arrow), as well as poor interface with host tissue (orange arrow) influence cell invasion, even though other areas of the gel are efficiently invaded (light green arrow) (E). The differential patterns of cell invasion into the same hydrogel hence strongly suggest that the host microenvironment surround the ECM material has a significant influence on cell invasion (F). Nevertheless even if there are blind spots within the hydrogel and areas of poor cell invasion at the host-gel interface, invading cells will find channels (yellow arrows) to move towards the center of mass (i) and are likely to continue their migration in the absence of encountering other cells (G). Scale bars are 5000 μm. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
