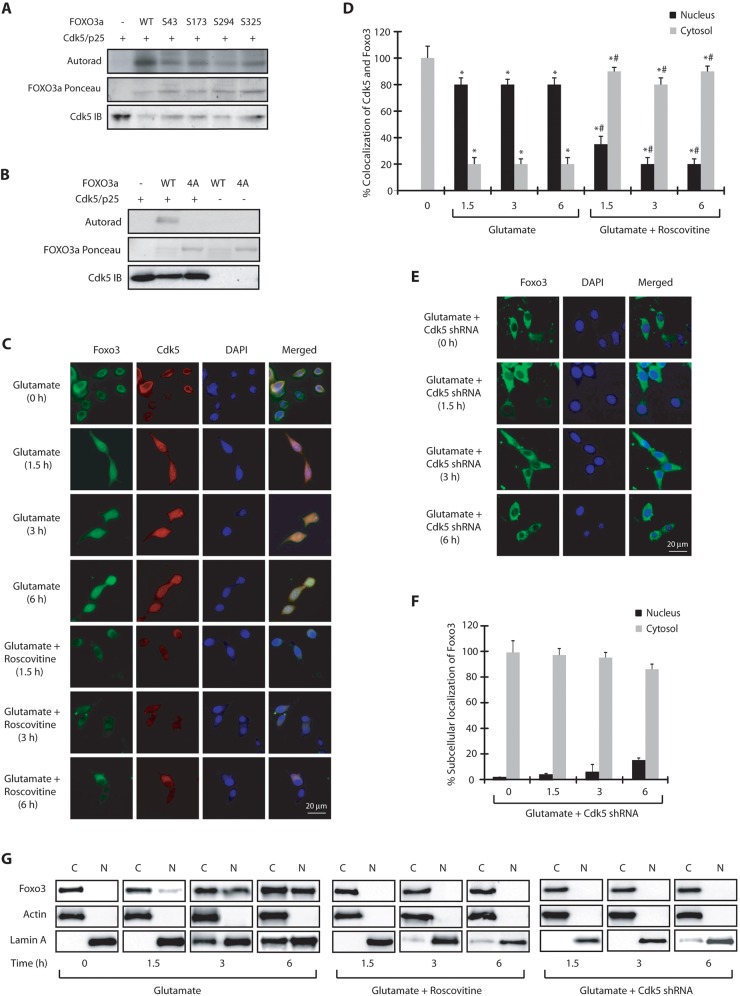
Fig. 3.
Cdk5 directly phosphorylates FOXO3a at multiple sites. (A) The Cdk5–p25 complex (Cdk5/p25) phosphorylates FOXO3a at S43, S173, S294 and S325 (human numbering). Recombinant 6×-His-tagged wild-type and FOXO3a mutants were subjected to a kinase assay with Cdk5–p25. (B) Cdk5 does not phosphorylate the quadruple 4A-FOXO3a mutant. (C) Glutamate stimulates nuclear translocation of Cdk5 and FOXO3a in FOXO3a-HT22 cells. FOXO3a-HT22 cells were treated with glutamate for 0–6 h, followed by immunostaining. Representative pictures are shown. (D) The percentage of cells showing nuclear translocation of Cdk5 and Foxo3. *P<0.01, compared with untreated HT22 cells; #P<0.01, compared with corresponding glutamate-treated HT22 cells (Student's t-test). (E) Cdk5-shRNA-infected HT22 cells were treated with glutamate (0–6 h). Representative pictures are shown. (F) The percentage of cells showing nuclear translocation of Foxo3. (G) Subcellular fractionation of Foxo3 in glutamate-treated FOXO3a-HT22 cells in the absence or presence of roscovitine or Cdk5 shRNA. Actin is the cytoplasmic marker and lamin A is the nuclear marker. N, nuclear fraction; C, cytoplasmic fraction. Graphical results are mean±s.e.m. Each experiment was repeated at least three independent times.