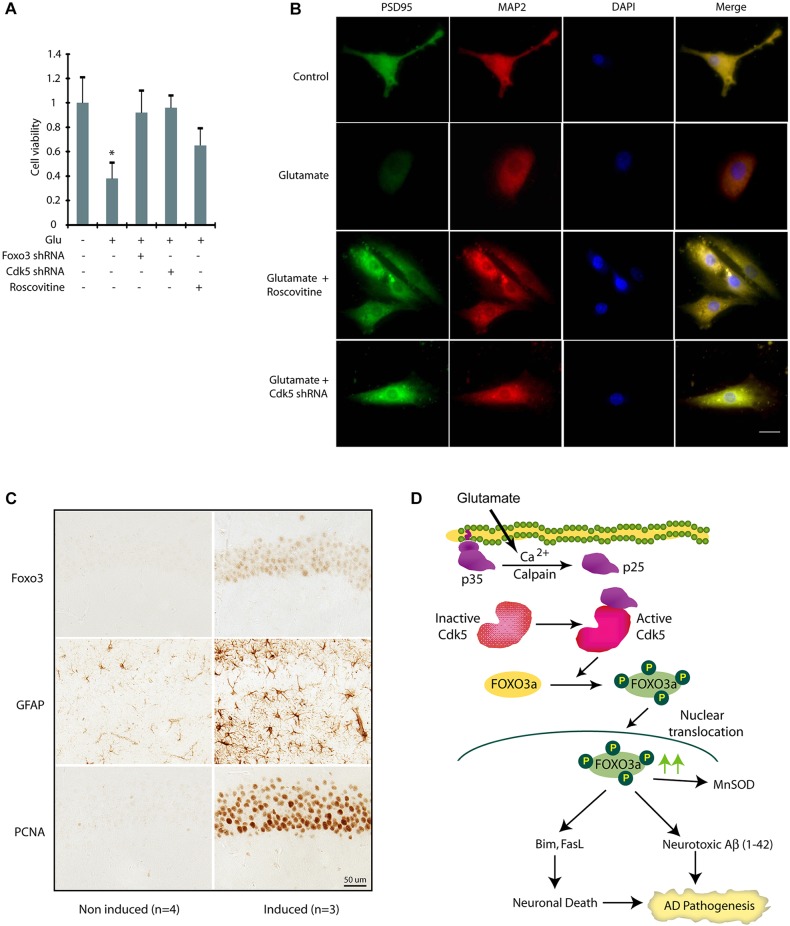
Fig. 8.
Cdk5 deregulation due to p25 expression promotes increased expression and nuclear localization of Foxo3 in vivo. (A) Inhibition and ablation of Cdk5 inhibits neurotoxicity in primary cortical neurons. Cdk5-shRNA- or Foxo3-shRNA-infected primary neurons (30 h) were treated with glutamate (24 h). Cell viability was tested by an MTT assay. *P<0.01, compared with untreated neurons (Student's t-test). (B) Primary cortical neurons pre-treated with roscovitine or Cdk5 shRNA were treated with glutamate for 12 h, followed by immunostaining with PSD95 or MAP2 and DAPI. Representative pictures are shown. Scale bar: 20 µm. (C) The increased expression and nuclear localization of Foxo3 in hippocampal neurons in p25 transgenic mice. After the induction of p25 for 2 weeks, the level of Foxo3 in nuclei of the hippocampal CA1 neurons is significantly increased (P<0.05, Student's t-test). Astrocytosis (GFAP) and cell cycle re-entry (PCNA) are also highly induced in the same area which is consistent with previously published findings and indicates Foxo3 is correlated with other early pathological changes induced by p25 overexpression. (D) Our model showing that Cdk5-mediated Foxo3 activation contributes to two hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease.