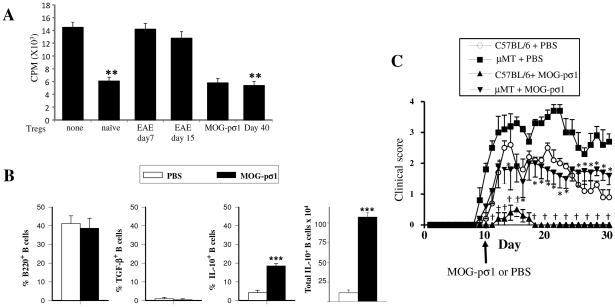
Figure 1.
EAE derived Tregs are dysfunctional and B cells modulate EAE. (A) Tregs were purified from naïve or EAE mice (day 7 or 15 p.ch., scores 1 and 3 respectively), MOG-pσ1-treated mice (day 15 p.ch.), those naturally recovering from EAE (day 40, scores 0-1), and CD25− CD4+ Teff cells from naïve mice. Tregs were then co-cultured with Teff cells (Tregs/effector ratio1:2) in the presence of anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28 mAbs for 4 days before measuring extent of proliferation using a 3H-thymidine incorporation assay. A representative experiment of 5 is shown; **p ≤ 0.01 versus naïve cell proliferation. (B) C57BL/6 mice (8/group) were induced with MOG35-55 EAE, and 10 days later, treated with PBS or MOG-pσ1. The percentage and total combined LN and splenic B220+ B cells expressing TGF-β+ or IL-10 from individual mice was measured 20 days p.ch.; ***p < 0.001 versus PBS-treated EAE mice. (C) C57BL/6 or B cell-deficient μMT mice were orally dosed with 50 μg MOG-pσ1 or PBS 10 days after EAE challenge and monitored daily for disease course. An average of 5 mice per group is represented; *p < 0.05 versus PBS-dosed μMT, †p < 0.05 versus PBS-dosed C57BL/6 mice.