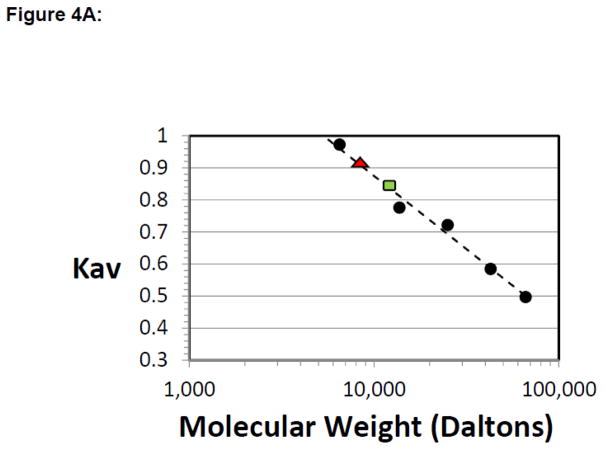
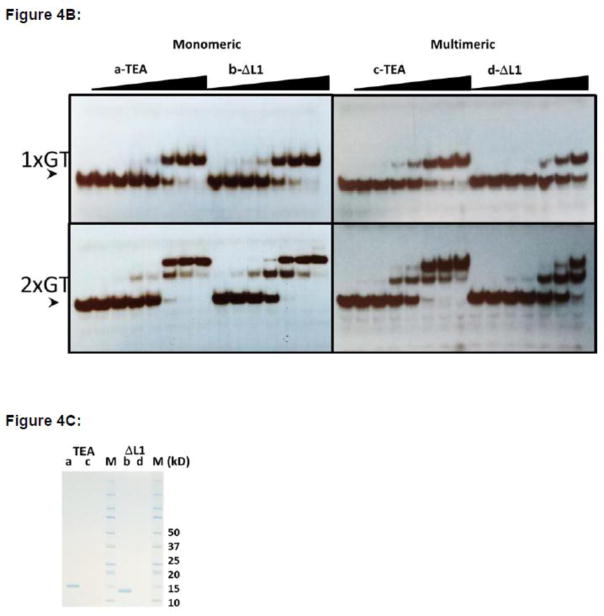
Figure 4. ΔL1 TEAD DBD exists largely in the monomeric form.
B. DNA binding by monomeric and multimeric fractions of TEAD DBD and ΔL1 TEAD DBD. Fractions from size exclusion chromatography that correspond to monomeric TEAD DBD (a), monomeric ΔL1 TEAD DBD, multimeric TEAD DBD (c), and multimeric ΔL1 TEAD DBD (d) were used for EMSA. Arrowhead indicates free DNA at 2 fmol/lane. Protein concentrations: lane 1: 0; lanes 2–8 & 9–15: 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300 nM.
C. SDS-PAGE of the four samples used for EMSA and molecular weight markers (M) (Bio-Rad, Kaleidoscope). (kD): Molecular weights of markers in kilodaltons.