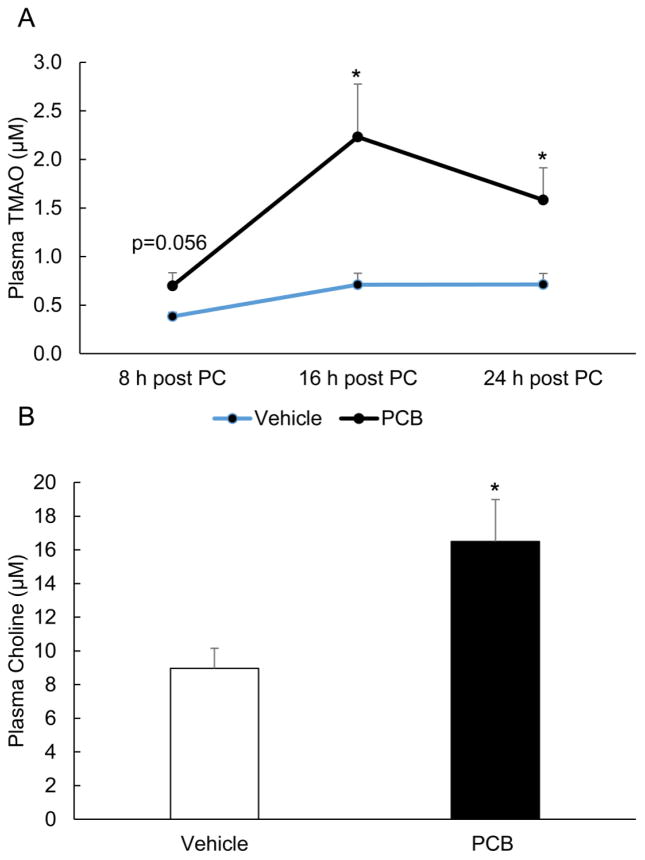
Figure 3.
Exposure to PCB 126 leads to sustained increases in plasma levels of TMAO after administration of dietary precursors. Mice were exposed to either vehicle oil or PCB 126 and 48 h later administered a dietary choline source. Plasma was collected at the indicated times for TMAO quantification (A) and levels were measured by HPLC/MS MS. For choline measurements (B), plasma was collected at the conclusion of the study and levels were measured by HPLC/MS MS. MRM transitions monitored included: TMAO-76/59.1, Choline-104.2/60.1, and d9-choline-113.1/69.1. AUC integration values were determined and all results were normalized to d9-choline internal standard values. Data are presented as mean±S.E.M. (*p<0.05, n=5 for each group, Student’s t-test).