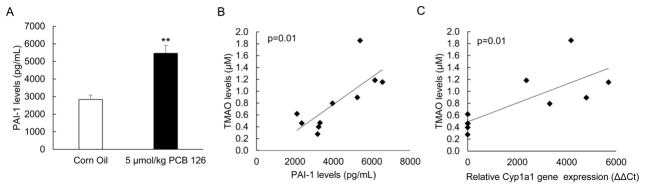
Figure 5.
AhR-mediated inflammatory genes are increased in PCB exposed mice and are correlated with plasma TMAO levels (A) Plasma levels of Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), a known risk factor for atherosclerosis, was significantly increased in mice exposed to PCB 126. Plasma was collected at the end of the study and PAI-1 total levels were identified using the Magpix system. All data are presented as mean±S.E.M (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, n=5 for each group, Student’s t-test). (B) Plasma PAI-1 levels were plotted against plasma TMAO levels for each mouse (n=5 for each group) and a linear goodness of fit was determined (linear regression). A statistically significant positive correlation between PAI-1 protein levels and plasma TMAO levels was determined (R=0.76, R2=0.57, p=0.01). (C) Relative gene expression values as determined by ΔΔCt method for AhR-target gene Cyp1a1 were plotted against plasma TMAO levels for each mouse (n=5 for each group) and a linear goodness of fit was determined (linear regression). A statistically significant positive correlation between liver Cyp1a1 relative gene expression levels and plasma TMAO levels was determined (R=0.76, R2=0.57, p=0.012).