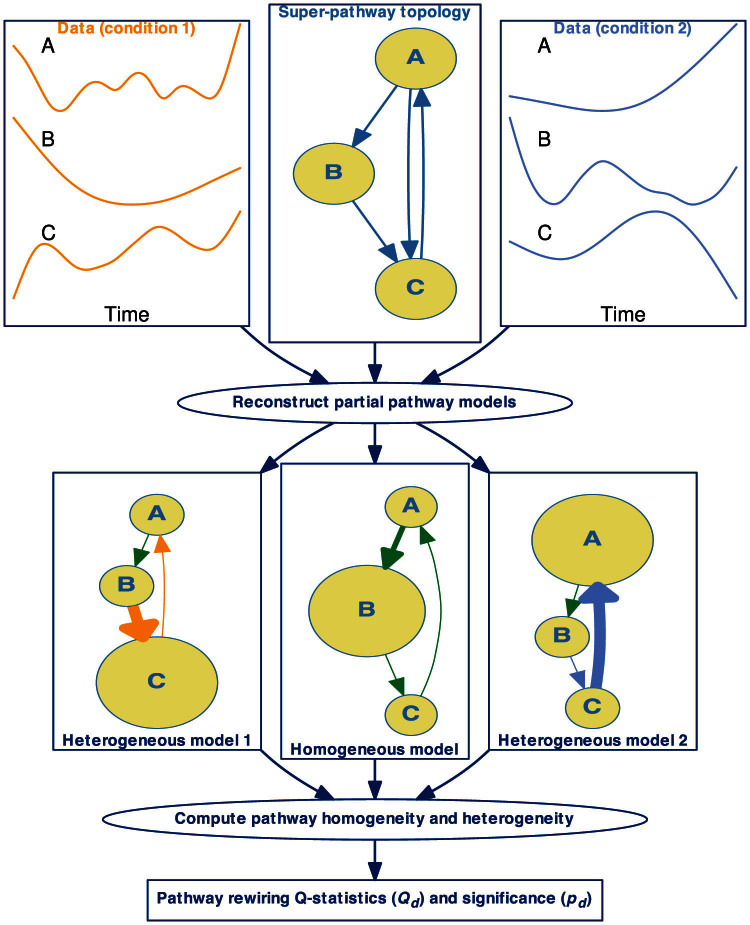
Figure 1. Overview of the Q-method for detecting pathway rewiring.
The input requires observed time course data from a pathway under multiple conditions. The input also includes a super-pathway topology, which can be either retrieved from a pathway topology database or causally inferred from the observed data. The first main step is to reconstruct partial pathway models – heterogeneous differential equation models specific to each condition. The strength of interaction heterogeneity is calculated for each node. Also a homogenous differential equation model is created from data pooled from all conditions. The second main step is to compute pathway interaction heterogeneity and homogeneity statistics and their statistical significance. The final output is thus a set of statistics, including Qd and pd measuring the strength and statistical significance of mechanistic pathway rewiring. The thickness of edges and the size of nodes indicate the strength of rewiring in the heterogeneous models; they indicate conservation in the homogeneous model.