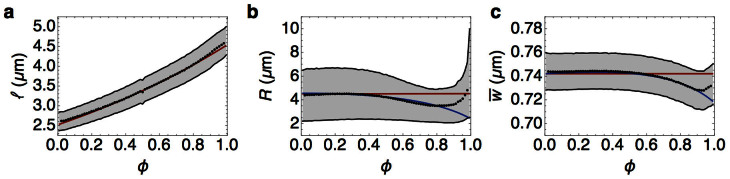
Figure 2. Dynamics of cell shape parameters.
(a) Length of the cell medial axis (data shown in black and exponential fit from our mechanical model in red). (b) Radius of curvature of the cell medial axis, obtained by calculating the best-fit circle to the entire cell (black points), with a time-averaged mean 〈R〉 = 4.44 ± 2.12 μm (0 < ϕ < 0.5). The mean-field model predicts a constant steady-state value for 〈R(ϕ)〉 (red solid line), whereas by accounting for constriction dynamics, the model captures the dip in 〈R(ϕ)〉 seen for 0.5 < ϕ < 0.9 (blue solid line). (c) Characteristic cell width, obtained by spatially averaging the width at each time point (black points), with a time-averaged mean 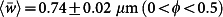 . The mean field model predicts a constant steady-state value for
. The mean field model predicts a constant steady-state value for 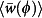 (red solid line), whereas cell constriction accounts for the dip in
(red solid line), whereas cell constriction accounts for the dip in 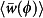 seen for ϕ > 0.5 (blue solid line). The shaded regions represent ±1 standard deviation. Model parameters: P = 0.3 MPa, γ = 50 nN/μm, kc = 2 nNμm2, Rc = 0.5 μm, km = 40 nNμm, Rm = 0.31 μm, τ = 73 min.
seen for ϕ > 0.5 (blue solid line). The shaded regions represent ±1 standard deviation. Model parameters: P = 0.3 MPa, γ = 50 nN/μm, kc = 2 nNμm2, Rc = 0.5 μm, km = 40 nNμm, Rm = 0.31 μm, τ = 73 min.