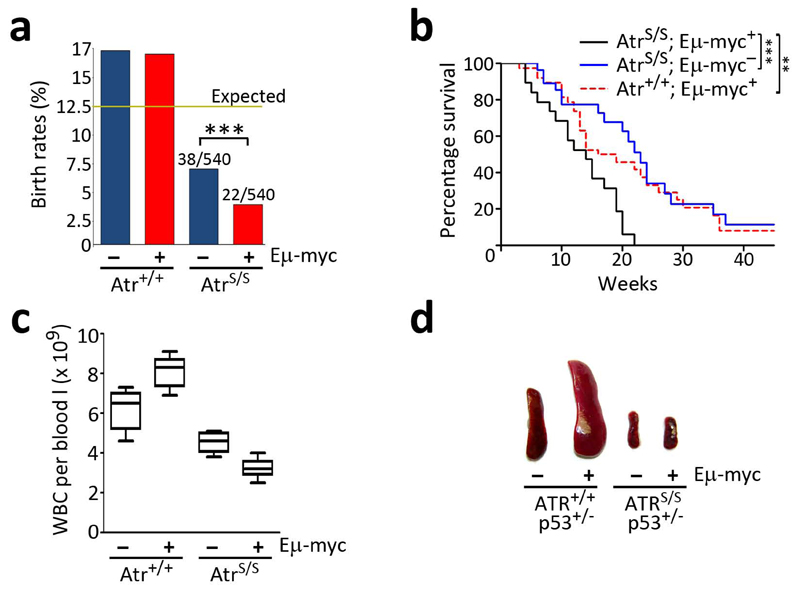
Fig. 1.
Reduced levels of Atr prevent lymphomagenesis on Eμ-myc mice. (a) Observed birth rates of the different genotypes obtained from Atr+/S; Eμ-myc+ x Atr+/S; Eμ-myc- crosses (n = 512 mice; χ2: P<0.001). (b) Kaplan Meyer analysis of the indicated genotypes (AtrS/S; Eμ-myc+: 24; Atr+/+; Eμ-myc+: 31; AtrS/S; Eμ-myc-: 32). The asterisks indicate the statistical significance of the different survival curves obtained in the Log- Rank Mantel-Cox Test. There was no significant difference between the survival of AtrS/S and Eμ-myc+ single mutants (p=0.48). (c) White blood cell (WBC) counts from 2 old month mice without detectable lymphoma (n=5). Note the expansion of the WBC compartment on Atr+/+; Eμ-myc+ mice, which contrasts with the further depletion of WBC when the Eμ-myc transgene is combined with Atr hypomorphism. (d) Photograph of the spleens of 5-week old mice illustrating the absence of splenomegalia on AtrS/S; Eμ-myc+; p53+/- mice. (*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001)