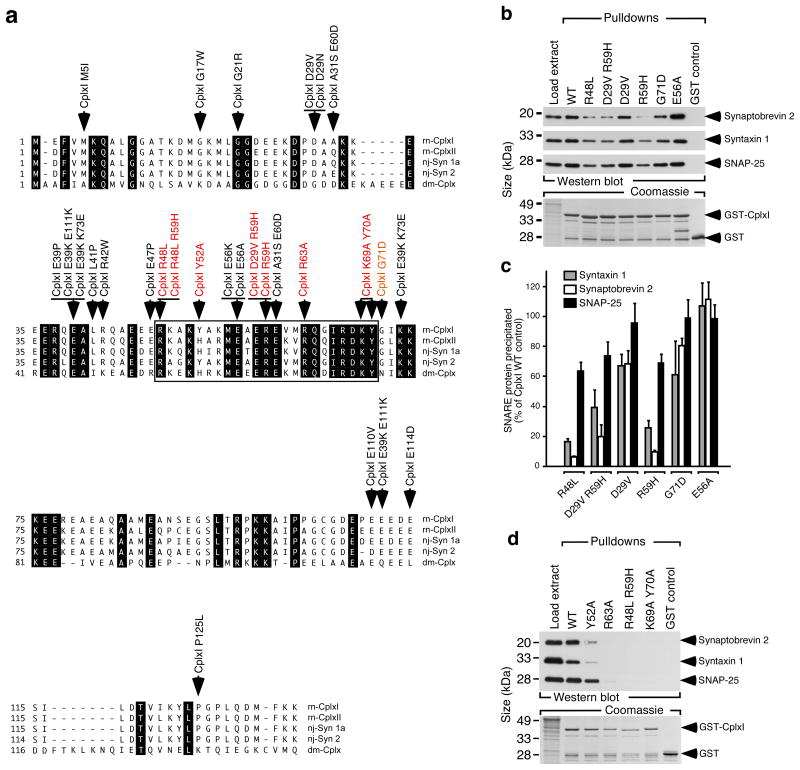
Figure 3. Identification of mutations in CplxI that block SNARE complex binding.
(a) The amino acid sequences of Rattus norvegicus (rn) CplxI and II, Narke japonica (nj) Synaphin 1a (Syn 1a) and Synaphin 2 (Syn 2), and Drosophila melanogaster (dm) Cplx are shown in single letter amino acid code and aligned for maximal homology. GenBank accession numbers are: NM_022864, rn CplxI; NM_053878, rn CplxII; AB004243, nj Syn 1a; AB004245, nj Syn 2; AY121629, dm Cplx. Identical residues are shown on black background. The boxed region indicates the SNARE complex binding region defined in rn CplxI (aa 48-70). Arrows indicate the single and double amino acid changes generated by mutagenesis (colored: mutations that cause changes in SNARE complex binding).
(b) Representative cosedimentation assays of WT GST-CplxI, mutant GST-CplxI (R48L, D29V R59H, D29V, R59H, G71D, E56A) fusion proteins and GST alone. Note that R48L, R59H, D29V R59H, and G71D showed reduced SNARE complex binding.
(c) Quantification of precipitated SNARE complex components by CplxI variants. Note that Synaptobrevin 2 and Syntaxin 1 were more strongly affected than SNAP-25 by the binding deficient CplxI mutants, indicating that under our experimental conditions CplxI binds to both trimeric SNARE complex and Synaptobrevin 2-Syntaxin 1 dimer. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3).
(d) Representative cosedimentation assays of WT GST-CplxI, mutant GST-CplxI (Y52A, R63A, R48L R59H, K69A Y70A) fusion proteins and GST alone (n=3). Note that Y52A showed a strong reduction of binding to the SNARE complex, whereas the SNARE complex bindings of R63A, R48L R59H and K69A Y70A were abolished.