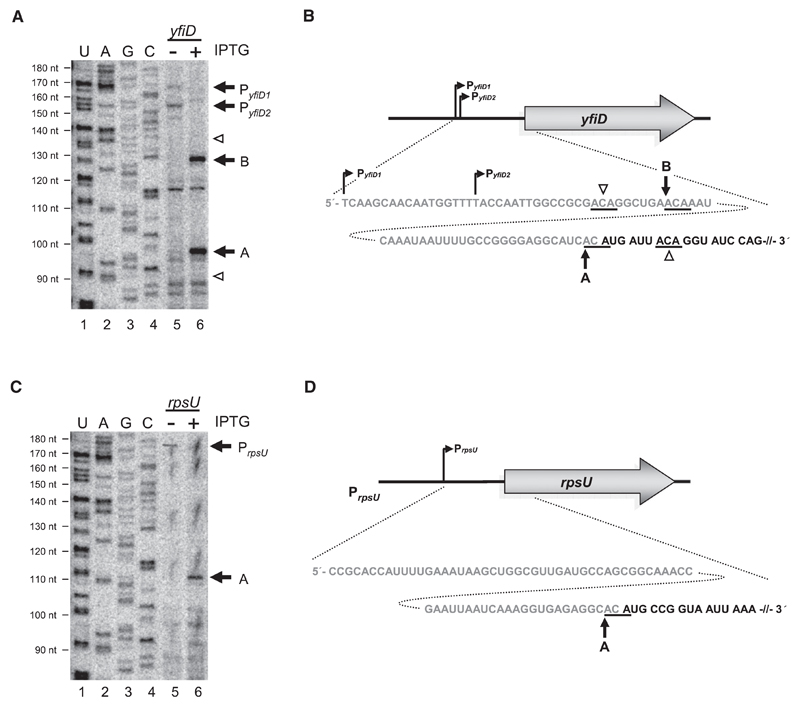
Figure 1. Determination of MazF Cleavage Sites on yfiD and rpsU mRNAs In Vivo and Schematic Depiction of Genomic Organization, 5′UTRs, and Proximal Coding Regions of the Respective mRNAs.
(A and C) Primer extensions employing primers (Table S1) specific for yfiD mRNA (A) and rpsU mRNA (C) performed on total RNA purified from E. coli strain MC4100relA+ comprising plasmid pSA1 without (lane 5) or with (lane 6) mazF overexpression. Extension signals corresponding to transcriptional start points of yfiD mRNA (PyfiD1 and PyfiD2) and rpsU mRNA (PrpsU) are indicated by black arrows (lane 5). Signals corresponding to MazF cleavage are indicated by black arrows and labeled analogous to Figures 1B and 1D, where “A” designates cleavage directly upstream of the AUG start codon, resulting in formation of a lmRNA, and “B” indicates cleavage further upstream (lane 6). White arrowheads indicate ACA triplets not cleaved by MazF (lane 6). (Lanes 1–4) Sequencing reactions of 16S rRNA employing primer V43 (Table S1) to determine length of primer extension (indicated to the left).
(B and D) Schematic depictions of promoter positions and sequence of 5′UTRs (in gray) and proximal coding regions (in black) of yfiD mRNA (B) and rpsU mRNA (D). MazF cleavage sites are underlined and indicted by arrows. The cleavage site directly upstream of the AUG start codon is marked with “A.” The cleavage site further upstream is indicated by “B.” Potential ACA triplets where MazF cleavage does not occur are indicated by white arrowheads.
See also Figure S1.