Fig. 1.
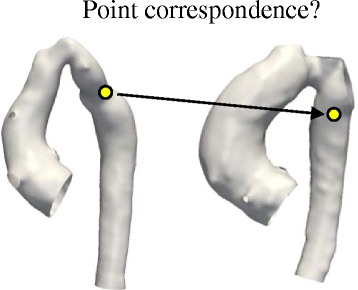
Point-to-point correspondence problem in complex cardiac morphologies. Widely used parametric methods to build statistical shape models are based on the so called Point Distribution Model (PDM) [5], in which shapes are parameterised by landmarks. Bookstein et al. [40] define landmarks as points on the structure’s surface for which “objectively meaningful and reproducible […] counterparts […]” exist in all other structures present in the dataset. In complex cardiac structures however, those point correspondences are difficult to establish, as illustrated here for two aortic arch models from the CoA cohort
