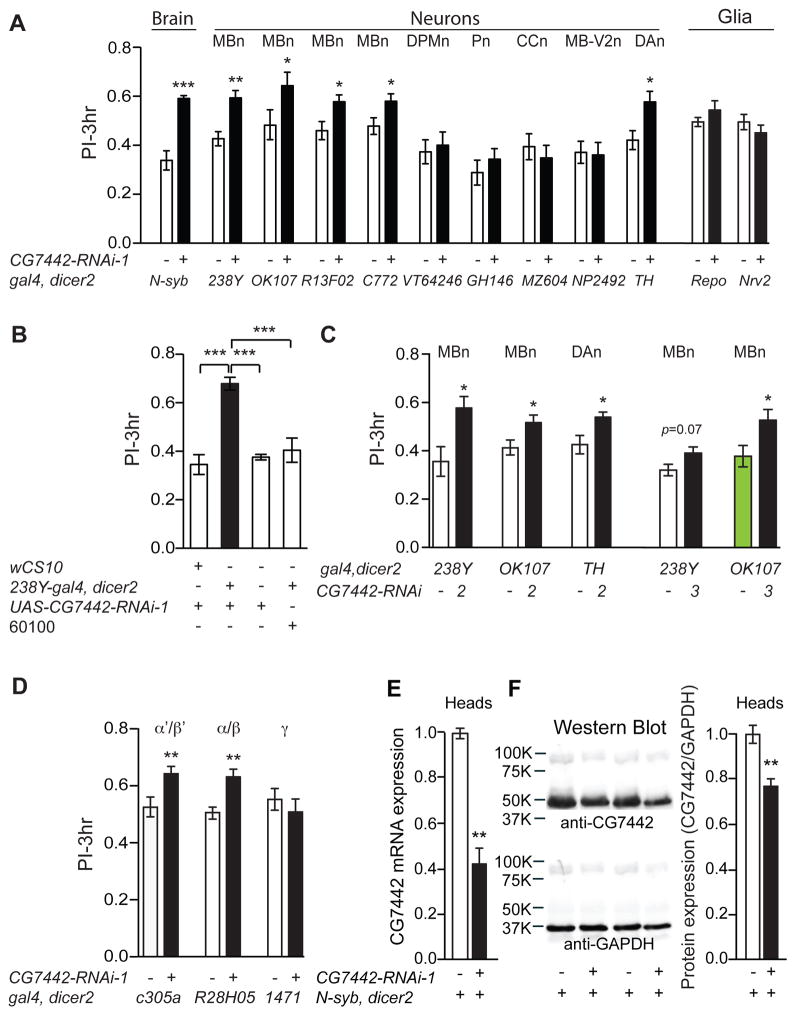
Figure 1. Memory suppression by CG7442 in MBn and DAn.
(A) RNAi-1 targeting gene CG7442 was tested along with the corresponding genetic control line (gal4/60100) for effects on 3h olfactory memory (PI=Performance Index) using a battery of gal4 drivers; N-syb-gal4 (pan-neuronal), 238Y-gal4 (all MBn neurons), OK107-gal4 (all MBn neurons), R13F02-gal4 (all MBn neurons), c772-gal4 (all MBn neurons), VT64246-gal4 (DPMn), GH146-gal4 (Pn), MZ604-gal4 (CCn), NP2492-gal4 (MB-V2n), TH-gal4 (DAn), repo-gal4 (pan glia), and Nrv2-gal4 (cortex and subperineurial glia). (B) Memory enhancement with 238Y-gal4 occurred only in bigenic flies containing the gal4 and RNAi-1 transgenes. (C) Memory expression was enhanced using two other RNAi transgenes directed against CG7442, RNAi-2 and RNAi-3, confirming that the phenotype is due to CG7442 knockdown. (D) Memory expression was enhanced in flies expressing CG7442-RNAi-1 in the α′/β′ (c305a-gal4) and α/β (R28H05-gal4) MBn, but not in the γ MBn (1471-gal4). Statistics for panels A, C, D: Results are plotted as means ± SEM. Comparisons between each experimental group and its corresponding control group was performed using Student’s t-test. N=6–8 for each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Statistics for panel B: Results are plotted as the mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc comparisons with ***P<0.001. N=8 for each group. (E) Total RNA, extracted from the heads of control (N-syb>60100) and N-syb-driven CG7442 knockdown flies was used for qRT-PCR experiments. A ~60% reduction of CG7442 mRNA was measured in the knockdown flies. Triplicate measurements were performed on each of three biological replicates. Statistics: Results are plotted as the normalized mean ± SEM. Two-tailed student’s t-test with **P<0.01. (F) Representative western blots of head lysates probed with polyclonal antisera against CG7442. Quantification of the immunoreactivity from both control and N-syb driven knockdown flies measured a ~25% reduction of CG7442 protein in the knockdown flies (right panel). GAPDH immunodetection was used as protein loading control. The CG7442 band intensity was compared to that for GAPDH and then the control normalized to 1.0. Statistics: Results are plotted as the normalized mean ± SEM. Two-tailed student’s t-test with **P<0.01.