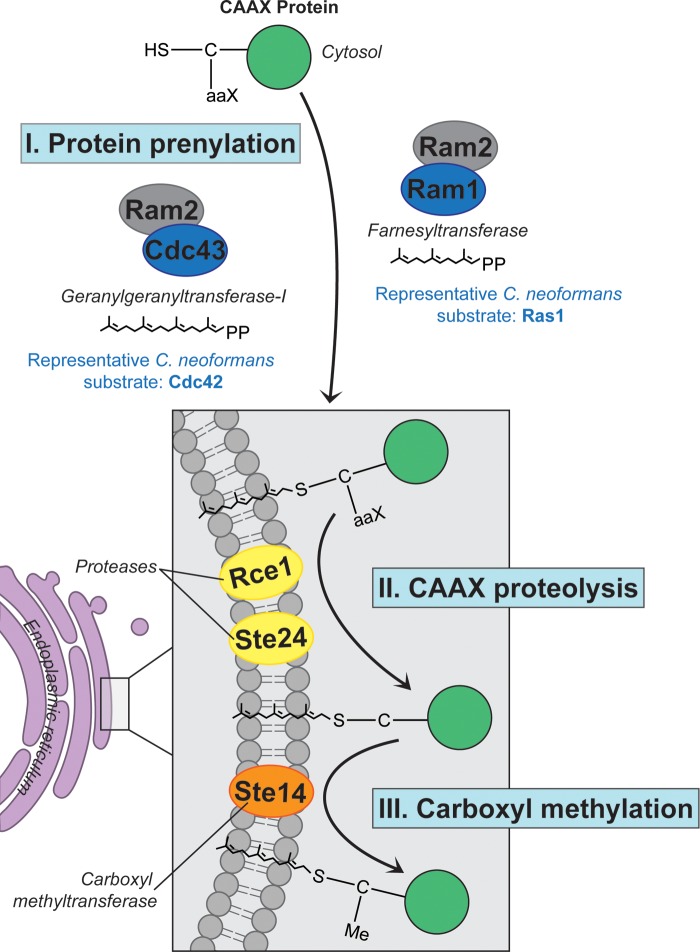
FIG 8 .
Model of prenylation and postprenylation processing in C. neoformans. CAAX proteins are (I) prenylated in the cytosol by the farnesyltransferase or geranylgeranyltransferase enzyme, resulting in initial membrane localization. Next, the prenylated protein undergoes further posttranslational modifications, including (II) cleaving of the C-terminal –AAX by the CAAX proteases Rce1 and Ste24, followed by (III) carboxyl methylation of the terminal cysteine by Ste14, after which they can be trafficked to their destined cellular membrane. In C. neoformans, substrate proteins may be trafficked to their destined cellular membrane through pathways independent of the CAAX proteases Rce1 and Ste24 and the carboxylmethyltransferase Ste14.