Figure 1.
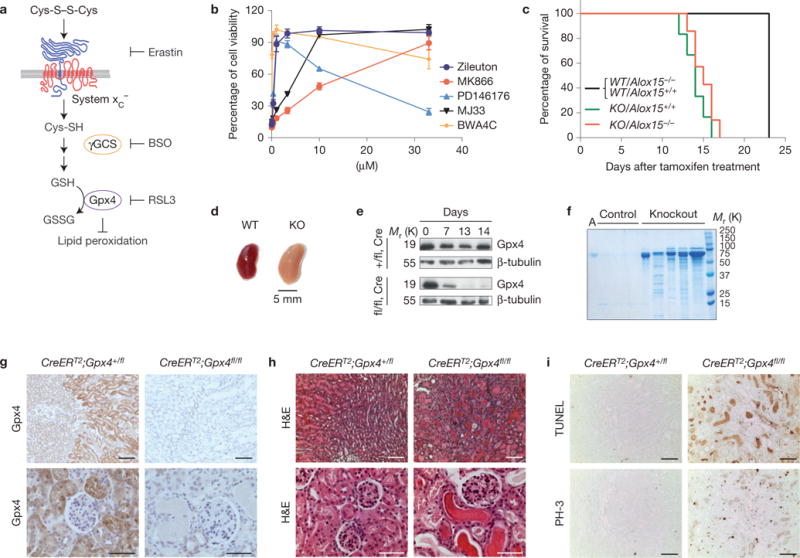
Inducible Gpx4 disruption causes ARF and death in mice. (a) A scheme showing the most important steps of glutathione (GSH) biosynthesis. αToc, α-tocopherol; BSO, L-buthionine sulphoximine; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; γGCS, γ-glutamylcysteine-synthase. (b) Inhibitors against enzymes of arachidonic acid metabolism prevent Gpx4-deletion-induced cell death in a dose-dependent manner. Gpx4 was disrupted in Pfa1 cells by the addition of 1 μM TAM in the presence of increasing concentrations of inhibitors. Cell viability was assessed by using AquaBluer 72 h after knockout induction. Data shown represent the mean ± s.d. of n = 4 of a 96-well plate from a representative experiment wells performed independently four times. (c) Mouse survival after TAM feeding. All induced Gpx4−/− (KO) mice died after approximately 2 weeks of TAM feeding regardless of Alox15 expression. None of the control mice (CreERT2;Gpx4+/fl/Alox15+/+(WT/Alox15+/+), CreERT2;Gpx4+/fl/Alox15−/−(WT/Alox15−/−)) died in the period investigated. Data are percentage of live animals; mean survival of Gpx4-null mice is 13.5 days after the onset of TAM feeding (n = 8 animals for KO/Alox15−/− and WT/Alox15−/− and n = 19 animals for KO/Alox15+/+ and WT/Alox15+/+). Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test: P <0.0001). (d) Overall kidney phenotype of TAM-treated CreERT2;Gpx4fl/fl animals (KO) at time of euthanization. Left, control kidney (TAM-treated CreERT2;Gpx4+/fl, WT); right, enlarged and pale Gpx4−/− kidney. (e) Western blot of whole kidney tissue extracts showing that Gpx4 was efficiently depleted on TAM feeding in CreERT2;Gpx4fl/fl (fl/fl,Cre), but not in control CreERT2;Gpx4+/fl (+/fl,Cre) mice. (f) TAM-inducible CreERT2;Gpx4fl/fl mice present massive albuminuria and unselective proteinuria compared with control mice. Each lane represents one knockout or control animal (A, murine albumin). (g) Immunohistochemical expression analysis of Gpx4 in kidney tissue revealed that Gpx4 was efficiently depleted on TAM treatment of CreERT2;Gpx4fl/fl mice, which is in line with the immunoblot data. Note the high expression of Gpx4 in tubule cells of kidney cortex, whereas glomeruli show only faint Gpx4 expression (bars top row 100 μm and bottom row 50 μm). (h) Histological analysis of kidneys of TAM-treated CreERT2;Gpx4fl/fl animals showed widespread tubular cell death, interstitial edema and proteinaceous casts in distal tubules (bars top row 100 μm and bottom row 50 μm). (i) The number of TUNEL+ cells and mitotic cells (phosho-histone H3 staining, PH-3) is increased in kidneys of symptomatic Gpx4−/− mice (bars 100 μm). Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8.
