Figure 2.
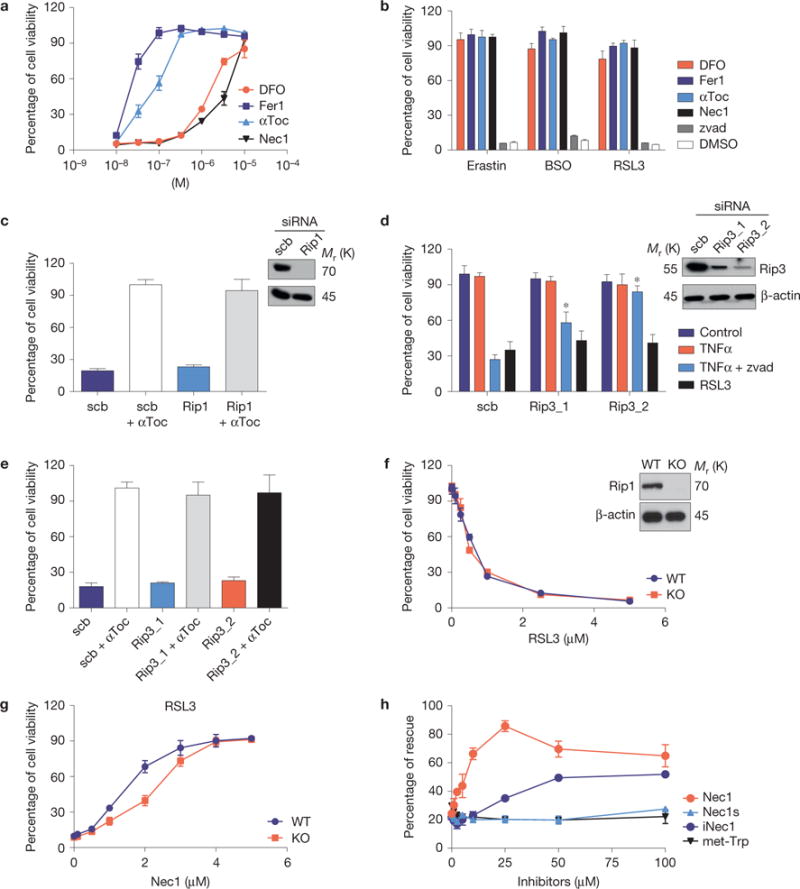
The inducible Gpx4 deletion in immortalized fibroblasts causes ferroptosis. (a) Cell death triggered by the inducible Gpx4 deletion in Pfa1 cells can be rescued by DFO, Fer1, αToc and Nec1 in a dose-dependent manner. Gpx4 was disrupted in Pfa1 cells as described in Fig. 1b (except for DFO, which was added 24 h after knockout induction, all inhibitors were added simultaneously along with TAM). Cell viability was assessed 72 h after knockout induction. (b) Cell death elicited in Gpx4-proficient Pfa-1 cells by the ferroptosis inducing agents (FINs) erastin (2.5 μM), BSO (20 μM) and RSL3 (20 nM) can be prevented by concomitant administration of DFO (10 μM), Fer1 (0.1 μM), αToc (1 μM) and Nec1 (20 μM), but not by the pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (50 μM, zvad). Cell viability was assessed 24 h thereafter. (c) Rip1 knockdown in Pfa1 cells is unable to protect against cell death induced by Gpx4 deficiency (scrambled, scb). Cells were transfected 6 h after knockout induction and cell viability was assessed 66 h later. (d) Rip3 knockdown attenuates TNFα/Z-VAD-FMK-induced necroptosis, but not RSL3-induced ferroptosis in L929 cells (Scb, scrambled). Knockdown was performed 48 h before addition of the cell death stimuli. Cell viability was assessed 6 h after TNFα (10 ng ml−1), TNFα + zvad (50 μM) or RSL3 (1 μM) treatment. Data shown in c and d represent the mean ± s.d. of n=3 wells of a 12-well plate from a representative experiment performed five times, P = 0.05 (one-way ANOVA). (e) Rip3 knockdown in Pfa1 cells does not rescue cell death induced by Gpx4 knockout (scrambled, scb). Cells were transfected 6 h after knockout induction and cell viability was determined 66 h later. (f) Although the Rip1 inhibitor Nec1 rescued cell death triggered by FINs, Rip1-knockout (KO) cells are equally as sensitive to the Gpx4 inhibitor RSL3 as Rip1 wild-type (WT) cells; cell viability was assessed 24 h after treatment. (g) Nec1 rescues RSL3 (1 μM)-induced cell death in both Rip1 KO and WT cells in a dose-dependent manner. Cells were pre-treated with increasing concentrations of Nec1 for 6 h and viability was assessed 24 h after treatment with FIN agents. (h) Structurally related analogues of Nec1 (Nec1s, iNec) and met-Trp, an inhibitor of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase that is also inhibited by Nec1, present different effects on cell death induced by Gpx4 deletion. Rescue was performed by treating cells with increasing concentrations of Nec1 analogues (0–100 μM), and cell viability was assessed 72 h after knockout induction. Data shown represent the mean ± s.d. of n = 3 wells (e,h) or n = 4 wells (a,b,f,g) of a 96-well plate from a representative experiment performed independently at least three times, P= 0.05 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test).
