Figure 1.
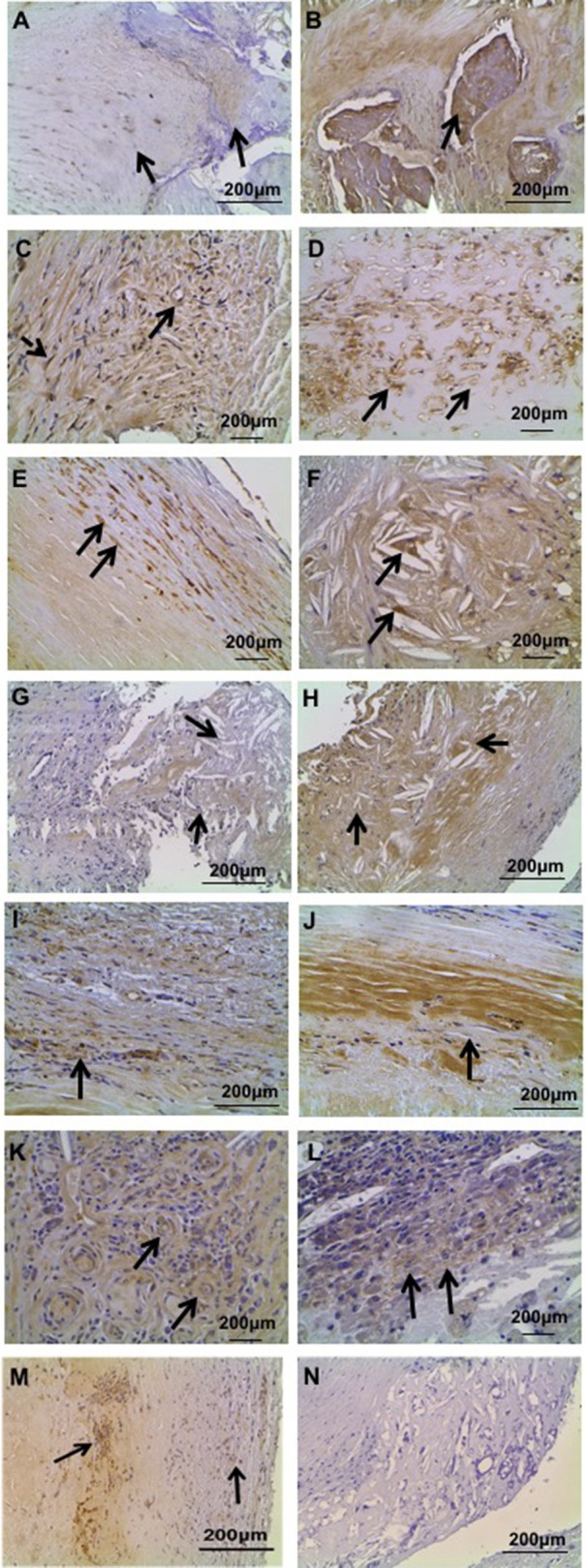
Representative immunohistochemical localization of UII, UT, and URP in human carotid plaque specimens. (A) UII immunoreactivity in stable carotid plaque: low intensity UII immunostaining in calcification (right arrow) and higher intensity immunostaining in myointimal cells (left arrow). (B) Strong UII immunoreactivity in calcified lesions of unstable carotid plaque. (C) UII staining in microvessels (bold arrow) and myointimal cells (dashed arrow) in stable carotid plaque. (D) Abundant UII staining in microvessels of unstable plaque. (E) UII staining in media SMCs of unstable plaque. (F) UII staining in foam cells of unstable plaque. (G) URP immunoreactivity in lipid core and surrounding cholesterol clefts (arrows) in stable carotid plaque. (H) Strong URP immunoreactivity in lipid core of unstable carotid plaque. (I) URP immunoreactivity in fibrosis of stable plaque. (J) Elevated URP immunoreactivity in fibrosis of unstable plaque. (K) URP staining in microvessels of unstable plaque. (L) URP staining in inflammatory cells of unstable plaque. (M) Abundant UT immunoreactivity in myointimal cells (right arrow) and calcium deposition (left arrow). (N) Negative control section of lipid and myointimal cells immunostained with normal serum showing no immunoreactivity.
