Figure 2. Estimates of body water and the osmotic and sodium volume of distribution in acute hypernatremia.
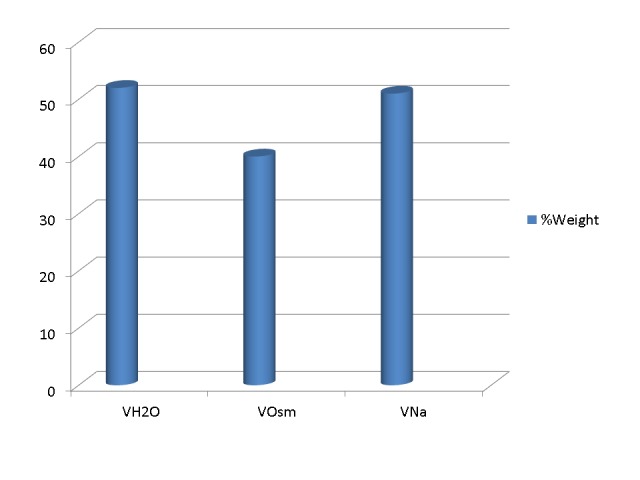
Shown here are the average estimates of body water (VH2O) measured by tritiated water dilution, the osmotic volume of distribution (VOsm) calculated by formula 11, and sodium volume of distribution (VNa) calculated by formula 12 in a study of anuric dogs infused with hypertonic saline [26]. The figure makes two points: (a) Even in acute hypertonicity, VOsm is substantially lower than VH2O and (b) VNa is equal to VH2O. The equality of VNa and VH2O provides the basis for applying equations 9 or 10 in the management of dysnatremias.
