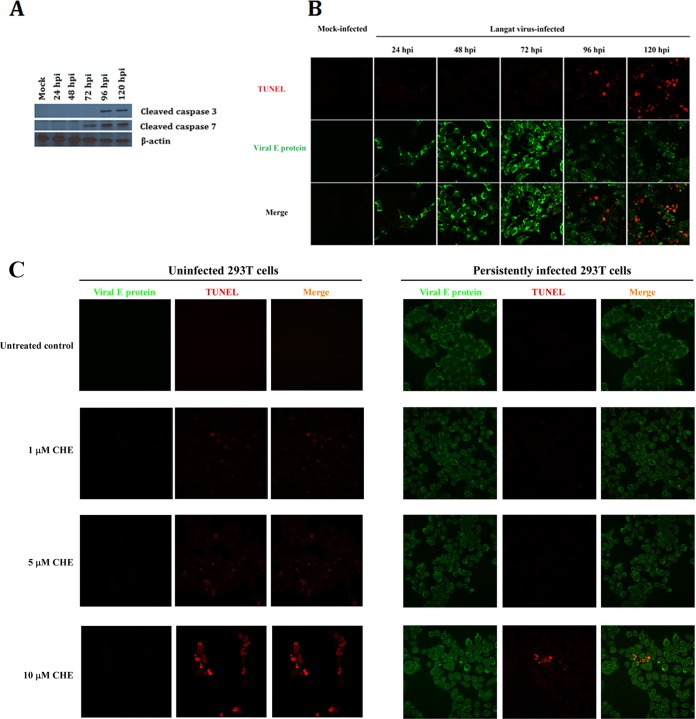
FIG 4 .
Characterization of the cell death mechanism of Langat virus-infected HEK 293T cells during acute infection. (A) Cleavage of effector caspases in acutely infected 293T cells. LGTV-infected cells were lysed in RIPA buffer and subjected to PAGE. Immunoblots were probed with mouse anti-caspase 3 and anti-caspase 7 antibodies followed by reaction with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled anti-mouse secondary antibody. Cleavage of caspases 3 and 7 was detected starting at 72 hpi. (B) Confocal microscopy images of TUNEL-stained ssDNA strand breaks (red stain) in Langat virus-infected (green stain) HEK 293T cells. ssDNA strand breaks were detected at 96 and 120 hpi (red nuclear staining). (C) Analysis of exogenous induction of apoptosis in uninfected and persistently infected 293T cells. Uninfected HEK 293T cells were sensitive to induction of apoptosis by all 3 concentrations of chelerythrine chloride (CHE) as shown by the presence of ssDNA breaks (red). Persistently infected cells were only minimally sensitive to induction of apoptosis by 10 µM CHE treatment.