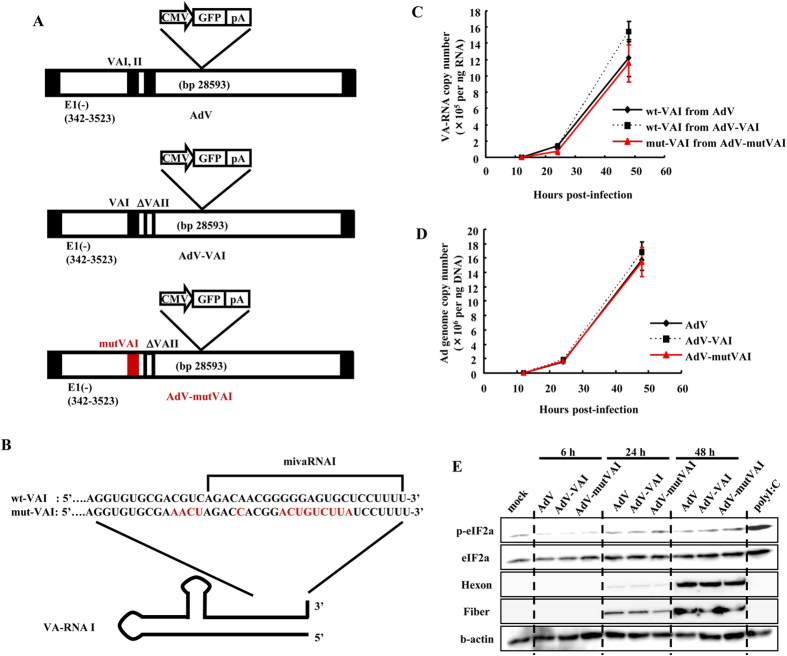
Figure 3. Characterization of an Ad mutant including mutated mivaRNAI sequence.
(A) A schematic diagram of AdV, AdV-VAI, and AdV-mutVAI. (B) A schematic diagram of the 3′-end sequences of wt-VAI and mut-VAI. (C) HEK293 cells were transduced with AdV, AdV-VAI, or AdV-mutVAI at an MOI of 1. At the indicated time points, expression levels of VA-RNAs were determined by real-time RT-PCR analysis. (D) HEK293 cells were transduced with AdV, AdV-VAI, or AdV-mutVAI at an MOI of 1. At the indicated time points, viral genome copy numbers of AdV, AdV-VAI, or AdV-mutVAI were determined by real-time PCR analysis. These data (C,D) are expressed as the means ± S.D. (n = 3). (E) Phosphorylated eIF2α protein levels following transduction with AdV, AdV-VAI, or AdV-mutVAI in HEK293 cells. The cells were transduced with AdV, AdV-VAI, or AdV-mutVAI at an MOI of 1 for the indicated hours. HEK293 cells was transfected with polyI:C (1 μg ml−1), followed by western blotting analysis after 6 h incubation. Hexon and fiber proteins are major Ad capsid proteins.