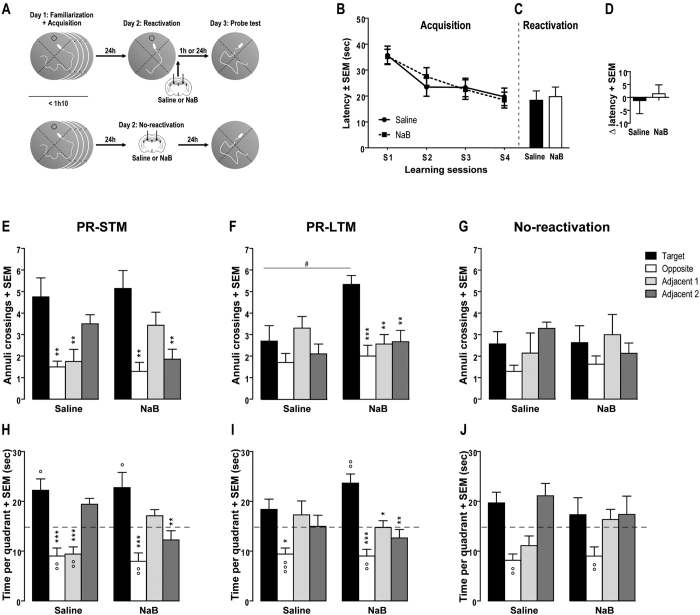
Figure 2. Intra-hippocampal injection of HDAC inhibitor after reactivation promotes post-reactivation spatial long term memory.
(A) Schematics of the experimental procedures. Mean latency (in sec) to find the platform during the four training sessions (B) and the reactivation trial (C) of the spatial Morris water maze task. Immediately after reactivation, mice received an intra-hippocampal injection of saline (n = 18) or NaB (n = 16). (D) Difference of latencies (Δ latency) between the last session of acquisition and the reactivation trial. (E–J) Number of annuli crossings (+SEM) and time spent in each quadrant (+SEM) during the 60-sec probe test given 1 h (E,H) or 24 h (F,I) post-reactivation, and without reactivation (G,J). The dotted line represents the chance level. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 target vs. others. °P < 0.05; °°P < 0.01 and °°°P < 0.001 quadrant vs. chance level (15 sec). #P < 0.05 target Saline vs. target NaB.