Fig. 4.
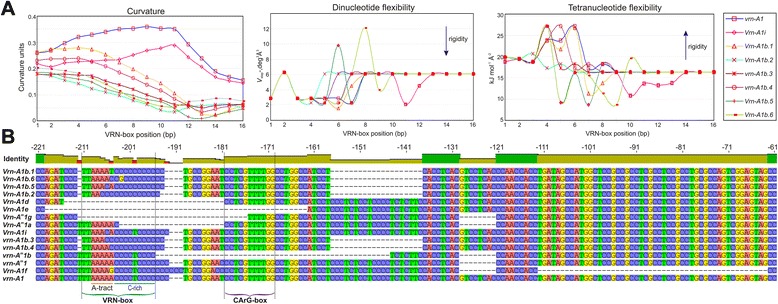
Polymorphism of the VRN-box differentiates the VRN-A1 alleles. a Distribution of local curvature, dinucleotide and tetranucleotide flexibility within the VRN-box for identified here Vrn-A1i and variants of Vrn-A1b. Arrows indicate increasing rigidity of the central dinucleotide steps. b Multiple alignments of VRN-A1 alleles carrying mutations within the promoter region (excluding Vrn-A1a); GenBank: KM047646 (Vrn-A1b.1), KT692944 (Vrn-A1b.6), KM047652 (Vrn-A1b.5), KM047641 (Vrn-A1b.2), AY616462 (Vrn-A1d), AY616463 (Vrn-A1e), DQ146422 (Vrn-A m 1g), AY244509 (Vrn-A m 1a), KM016790 (Vrn-A1i), KM047647 (vrn-A1b.3), KM047651 (vrn-A1b.4), EU875079 (vrn-A m 1b), KM016789 (vrn-A m 1), GQ451816 (Vrn-A1f), AY747600 (vrn-A1). The effect of deletion within Vrn-A1f on vernalization requirement is unclear. Positions are indicated relative to the vrn-A1 transcription start site
