Figure 2.
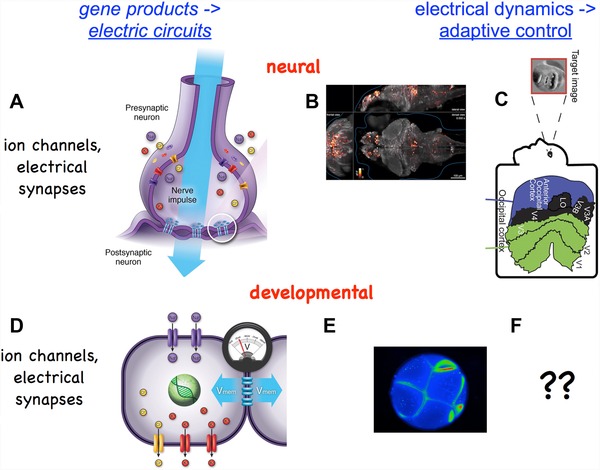
Bioelectric circuit elements in the brain and body. Gene loci encode ion channels and gap junction proteins (electrical synapses). However, it is the electrical dynamics of the resulting real‐time electric circuits that determine behavior of cells and tissues. In the brain, ion channels and electrical synapses (A) give rise to electrical activity in the brain (B) that integrates data, implements goal‐directed decision‐making behavior, and stores representations of geometric patterns. (C) On‐going efforts in a number of labs have shown that cognitive semantics of electrical brain states can be mathematically analyzed, such as computational pipelines that reveal which image a subject is visualizing mentally. In a highly parallel process, ion channels and gap junctions in non‐excitable cells (D) give rise to developmental bioelectricity―spatial and temporal patterns of resting potential occurring during development and regeneration (E). The ongoing effort to understand how developmental patterns are encoded in bioelectric properties (F) is the goal of cracking the bioelectric code. Images in panels A, D were made by Jeremy Guay of Peregrine Creative. Panel B used with permission from Ahrens et al., 2013. Panel C used with permission from Naselaris et al., 2009.
