Figure 1.
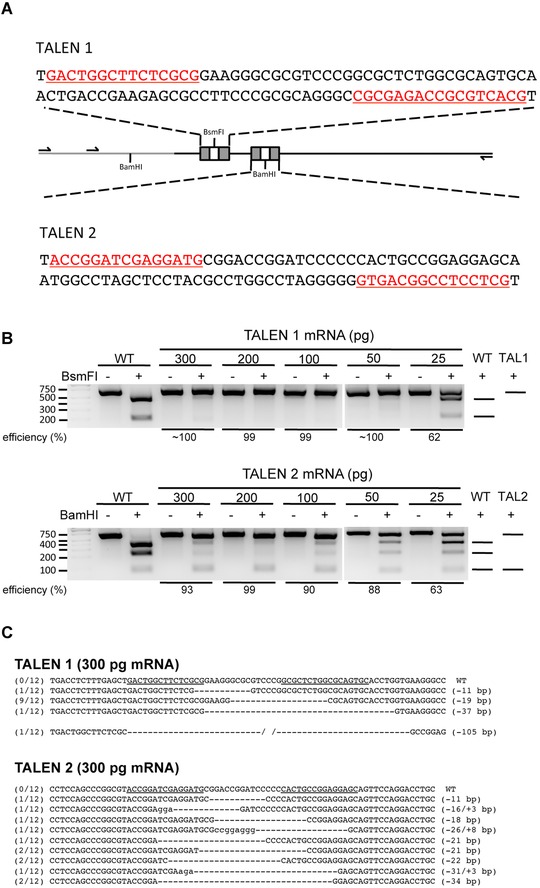
Editing axolotl tsp‐1 locus by TALENs. (A) Schematic of the exonic region in axolotl tsp‐1 locus and design of TALENs. The exonic region of tsp‐1 locus is indicated by the black line and the intronic region is indicated by the gray line. The binding sequences of the TALEN pairs used in this study are underlined and highlighted in red or marked as gray boxes. Primers used for PCR reactions are indicated by arrows, and the recognition sites of restriction enzymes used for determining efficiency of editing are noted. (B) Cleavage of PCR products by restriction enzymes indicates that the tsp‐1 locus has been edited. Genomic DNA from one embryo of WT (wild‐type; non‐injected) or TALEN mRNA injection is used for each lane. For each sample, an equal amount of PCR product, not incubated with the restriction enzyme, was loaded as an undigested control. The predicted patterns of DNA fragments after restriction enzyme digestion are shown on the right. First lane from the left is the DNA ladder. PCR amplicons from TALEN1 and TALEN2 mRNA‐injected embryos were cleaved by BsmFI or BamHI, respectively. (C) Sequencing results of the PCR amplicons from tsp‐1 locus of embryos injected with 300 pg TALEN mRNA, which shows various indel mutations in the tsp‐1‐TALEN target site. The numbers listed at the beginning of each sequence indicate the frequency of that sequence being detected among all sequenced amplicons for each embryo. Sequences recognized by TALEN pairs are underlined in WT sequences. Lower‐case letters indicate insertions.
