Figure 3.
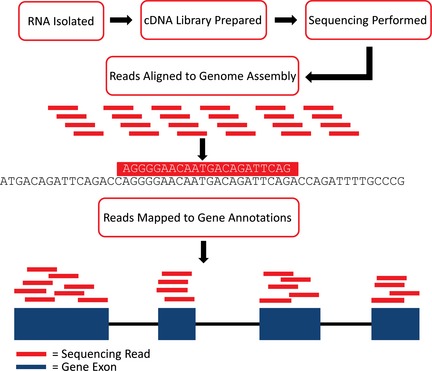
RNA‐Seq flowchart. Isolated RNA is converted to cDNA, a stable molecule, which can then be amplified and sequenced. Sequencing reads are then aligned to the genome assembly (sequence only) to identify their locations based on nucleotide matches. Mapping the reads to a gene annotation list will generate the number of sequencing reads that have aligned with a particular gene and are called counts. These counts at any particular gene are representative of the amount of gene expression in the sample and can be compared across horses to identify differentially expressed genes.
