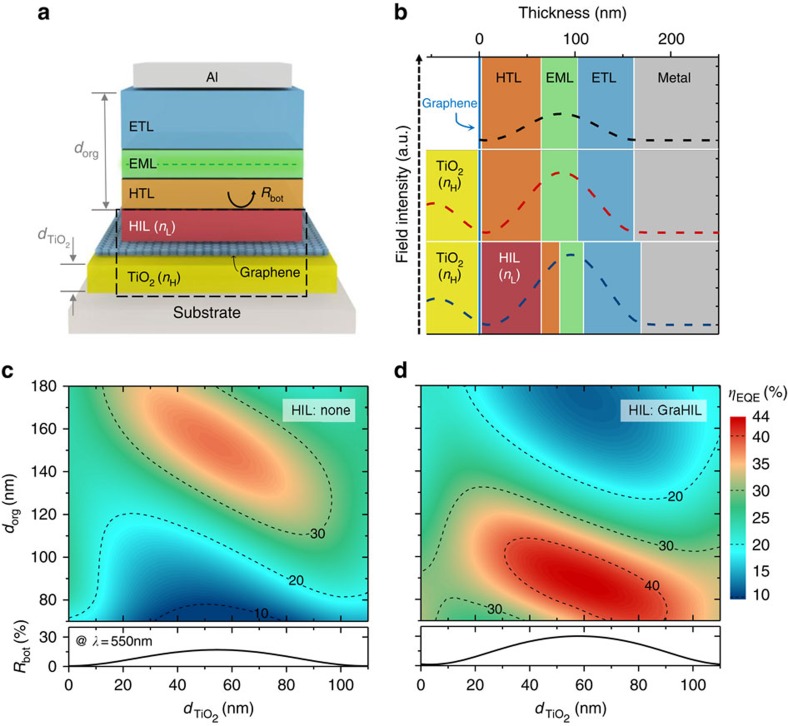
Figure 1. Design overview of proposed high-efficiency graphene-based OLEDs.
(a) Schematic device structure of the proposed OLEDs. (b) Electromagnetic field intensity distribution (dashed lines) of the OLEDs under study for their respective first-order cavity design. The field-intensity distribution of the graphene-based OLED without TiO2 is also shown for comparison for the case where the thickness values of organic layers are same as the OLEDs with TiO2 but without low-index HILs. (c,d) Calculated maximum external quantum efficiency (ηEQE) of graphene-based OLEDs with TiO2 under-layer as a function of TiO2 and organic layer thickness (dTiO2 and dorg, respectively). Dashed lines represent contour lines for ηEQE of 10, 20, 30 or 40% as indicated in the graph. (c) Without a low-index HIL; (d) with GraHIL as a low-index HIL. On the bottom of each case, the reflectance (Rbot) from the bottom electrode assembly (TiO2/graphene/(HIL)) as a whole is presented as a function of dTiO2 for light incident from the organic layers.