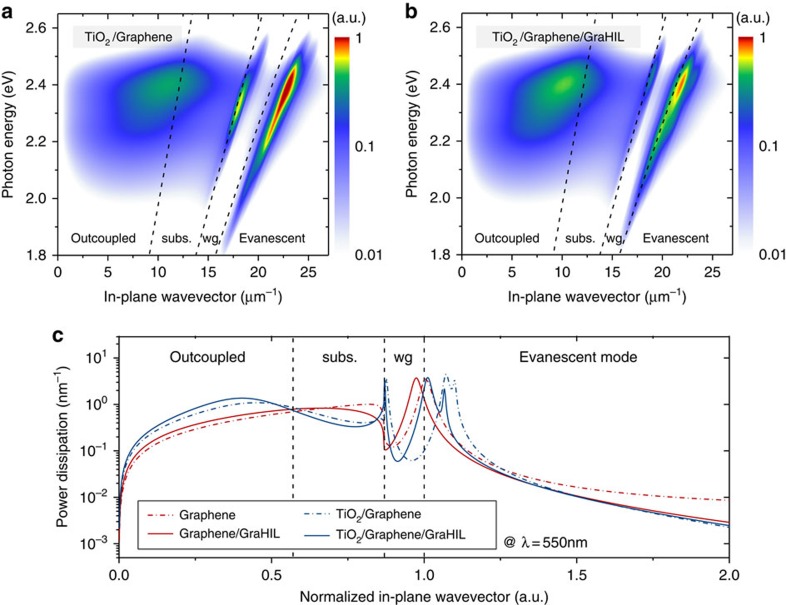
Figure 2. Synergetic optical effect of TiO2 as a high-index layer and GraHIL as a low-index HIL.
(a,b) Calculated power dissipation spectra weighted with the emitter spectrum in arbitrary units (mapped as a colour defined in the colour bars.) versus in-plane wave vector: (a) with TiO2 but without GraHIL; (b) with both TiO2 and GraHIL. The black dashed lines indicate border lines dividing representative optical modes including outcoupled, substrate-confined (subs), waveguided (wg) and evanescent modes. (c) Calculated power dissipation versus normalized in-plane wave vector at λ=550 nm for various electrode structures under study. For the devices with TiO2, dTiO2 was fixed at 55 nm and dorg was chosen for optimal conditions in each case. For the devices without TiO2, dorg was set at the same value as that of each counterpart in the devices with TiO2.