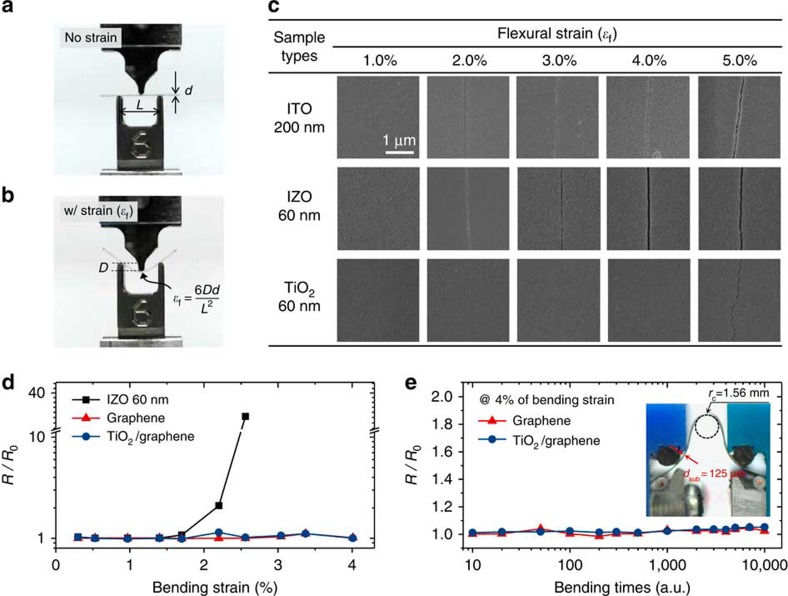
Figure 5. Flexural mechanical properties of TiO2 films and electrical properties of TiO2/Graphene under flexural strain.
(a,b) Images of the three-point bending-test set up (static loading) where flexural tensile strain (ɛf) is easily controlled via geometrical parameters shown in the pictures. (c) Scanning electron microscopy images for the top surfaces of 200-nm-thick ITO, 60-nm-thick IZO and 60 nm-thick TiO2 on PET substrates after static loading at a specified ɛf. (d) The sheet resistance (R) of IZO (60 nm), graphene, TiO2 (60 nm)/graphene on PET substrates as a function of flexural strain applied (measured after being bent 10 times at the specified strain (dynamic loading)). The sheet resistance is normalized to the initial value (R0). (e) R/R0 of graphene and TiO2 (60 nm)/graphene on PET substrates in relation to the number of bending cycles at flexural strain of 4%.