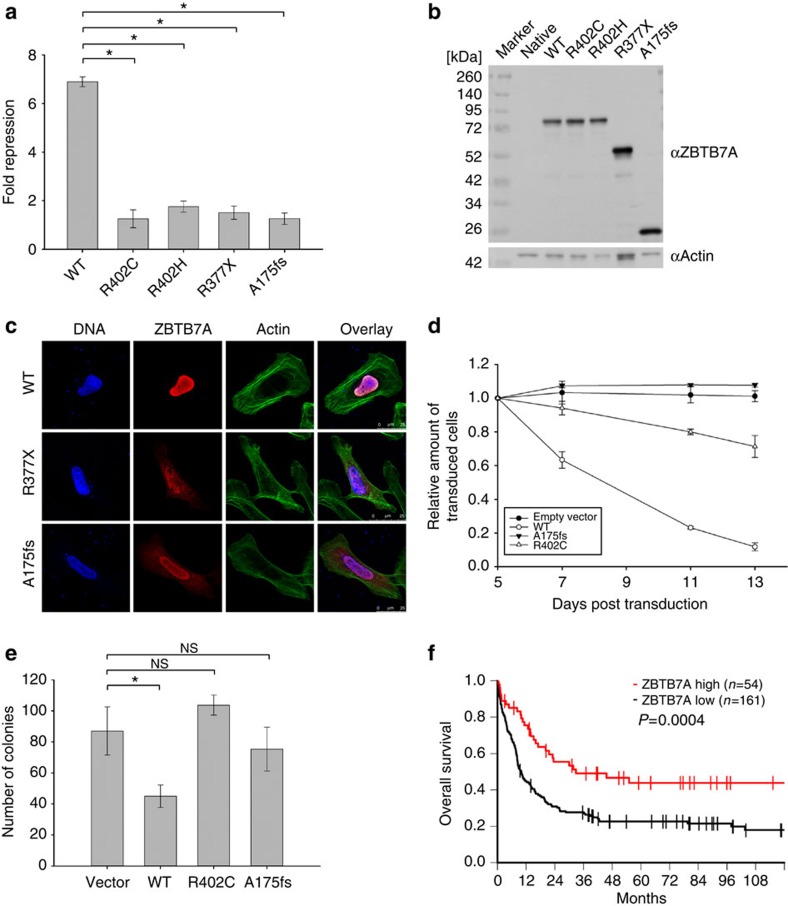
Figure 3. Functional consequences of ZBTB7A mutations and clinical relevance of ZBTB7A expression.
(a) Luciferase assay in transiently transfected HEK293T cells using the pGL2-p19ARF-Luc reporter combined with expression constructs for wild-type and mutant ZBTB7A. (b) Western blot of ZBTB7A constructs expressed in HEK293T cells. (c) Sub-cellular localization of ZBTB7A wild type, R377X and A175fs in transiently transfected U2OS cells. Scale bar, 25 μm. (d) Growth of Kasumi-1 cells stably expressing ZBTB7A wild type or mutants. (e) CFC assay of murine bone marrow lineage-negative cells co-expressing RUNX1/RUNX1T1 and wild-type or mutant ZBTB7A. (f) Overall survival of patients with CN-AML according to ZBTB7A expression (log-rank test, P=0.0004). *Two-tailed, unpaired Student's t-test, P<0.05; NS, not significant. Bar graphs or growth curves represent mean±s.d. of three independent experiments.