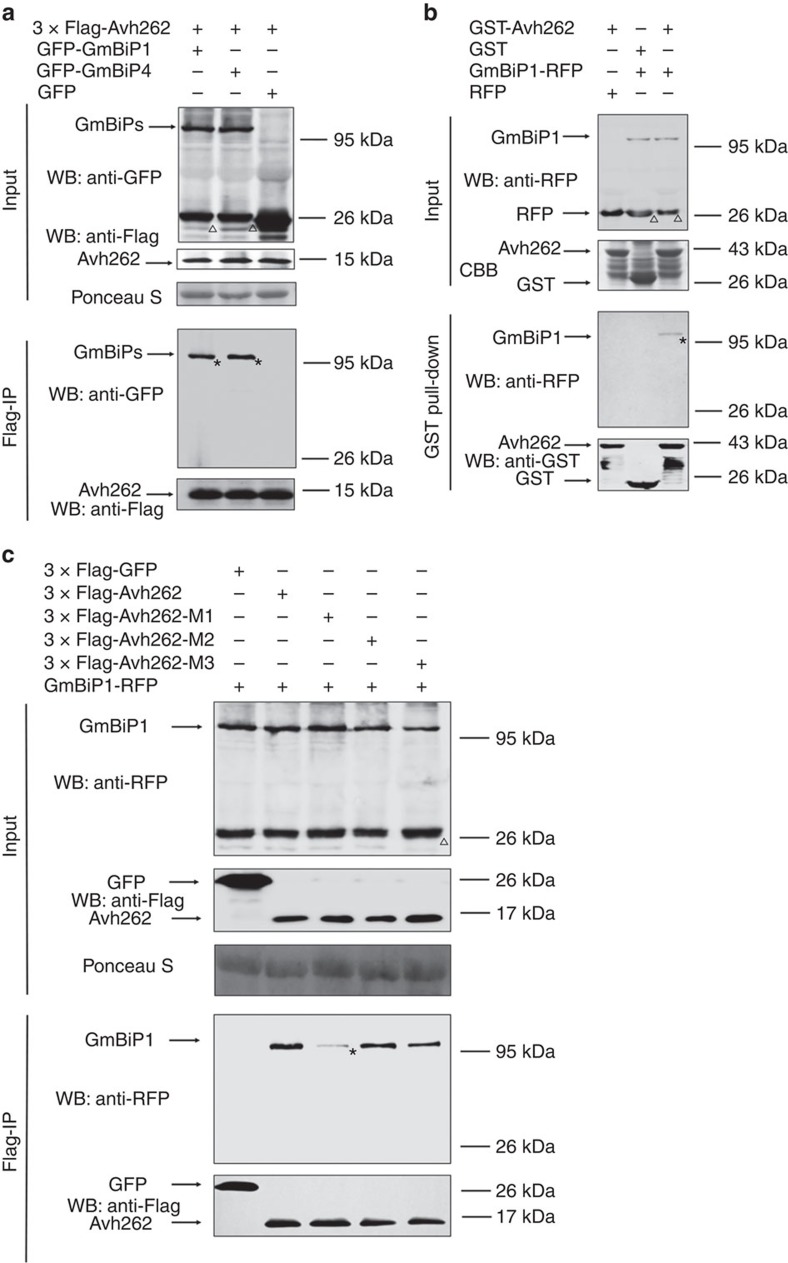
Figure 3. PsAvh262 interacts with plant endoplasmic reticulum luminal BiPs.
(a) PsAvh262 interacts with soybean BiPs in planta. Total proteins were extracted from N. benthamiana leaves expressing 3 × Flag-PsAvh262 together with GFP-GmBiP1 or GFP-GmBiP4 (GFP was attached to the N terminus of the signal peptides of the GmBiPs). Protein complexes were pulled down using anti-Flag agarose beads and the co-precipitation of GFP-GmBiP1 or GFP-GmBiP4 was detected by western blotting using an anti-GFP antibody. (b) Proteins extracted from N. benthamiana leaves expressing GmBiP1-RFP (RFP was fused to the C-terminal HDEL sequence of GmBiP1) or RFP were incubated with E. coli homogenate containing GST-PsAvh262 or GST. Enrichment of GmBiP1-RFP in GST-PsAvh262-bound glutathione resins was detected using an anti-RFP antibody. (c) M1 deletion greatly reduces the interaction of PsAvh262 with GmBiP1. 3 × Flag-PsAvh262 or its mutants were co-expressed in N. benthamiana with GmBiP1-RFP. Protein complexes were pulled down using anti-Flag agarose gel, and co-precipitations of PsAvh262 and its mutants with GmBiP1 were detected using immunoblots. Membranes were stained with Ponceau S to confirm equal loading. *, the objective bands of GmBiPs. Δ, non-specific bands of GmBiPs when using anti-GFP or anti-RFP, similar to GFP-PsAvh262 protein. Similar results were obtained in at least three independent experiments.