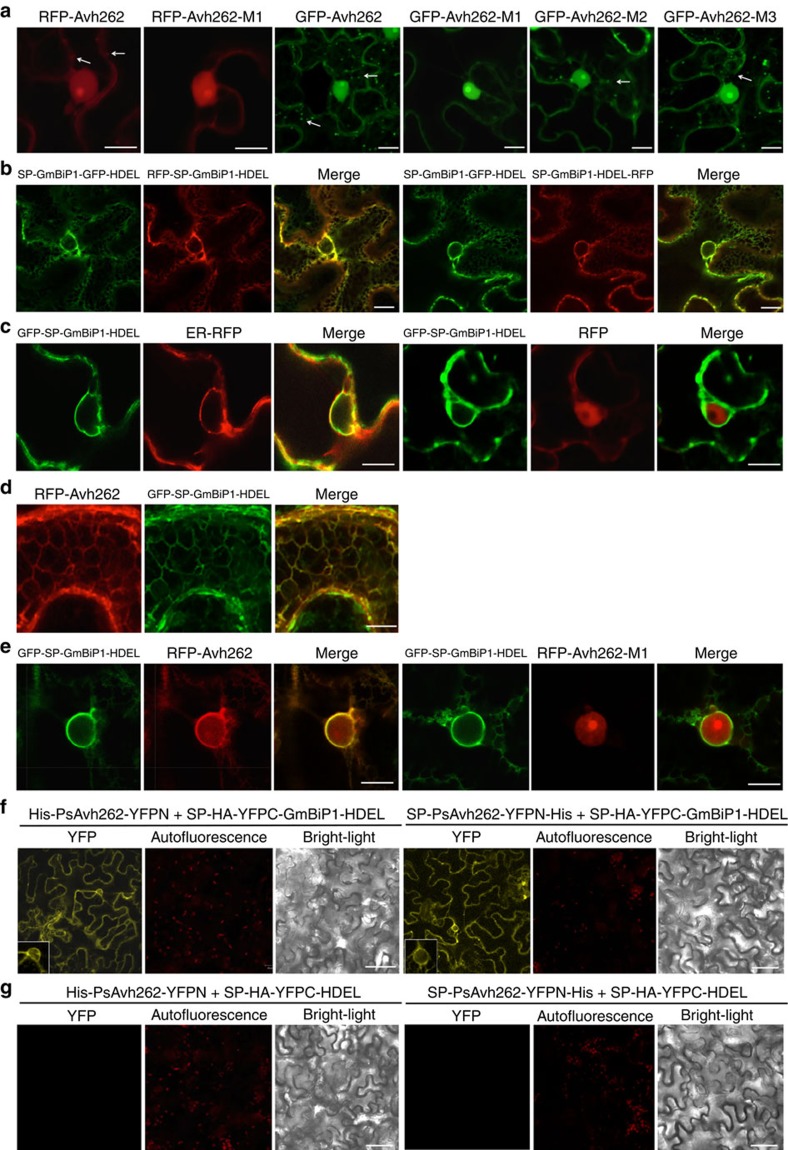
Figure 4. PsAvh262 and GmBiP1 co-localize to the endoplasmic reticulum.
In all panels, proteins were expressed in N. benthamiana through agroinfiltration. Fluorescence was detected in epidermal cells of the infiltrated leaves by confocal microscopy at 48 h after agroinfiltration. Scale bars, 10 μm. (a) Localization of RFP- and GFP-fusions of PsAvh262 and mutants in the absence of GmBiP1. FPs were attached to the N terminus of PsAvh262 without its signal peptide. PsAvh262 and mutants M2 and M3 were primarily located in the nucleus and nucleolus, but also in punctate structures in the cell cortex. RFP-PsAvh262-M1 was no longer present in cell cortex. (b,c) Localization of GmBiP1 FP fusions to the ER. GmBiP1 fusions were targeted to ER-like structures irrespective of the placement of the FP (b). GFP-SP-GmBiP1-HDEL co-localizes with SP-RFP-HDEL, but not with RFP (c). (d,e) RFP-PsAvh262 and GFP-SP-GmBiP1-HDEL co-localize to the ER. Co-localization to the ER network (d) and to the peri-nuclear ER (e). The M1 deletion eliminates co-localization to the peri-nuclear ER. (f,g) Co-localization of PsAvh262 and GmBiP1 detected by bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) using the constructs shown in Supplementary Fig. 7a. Complementation is only observed with GmBiP1 constructs (f) but not control constructs (g).