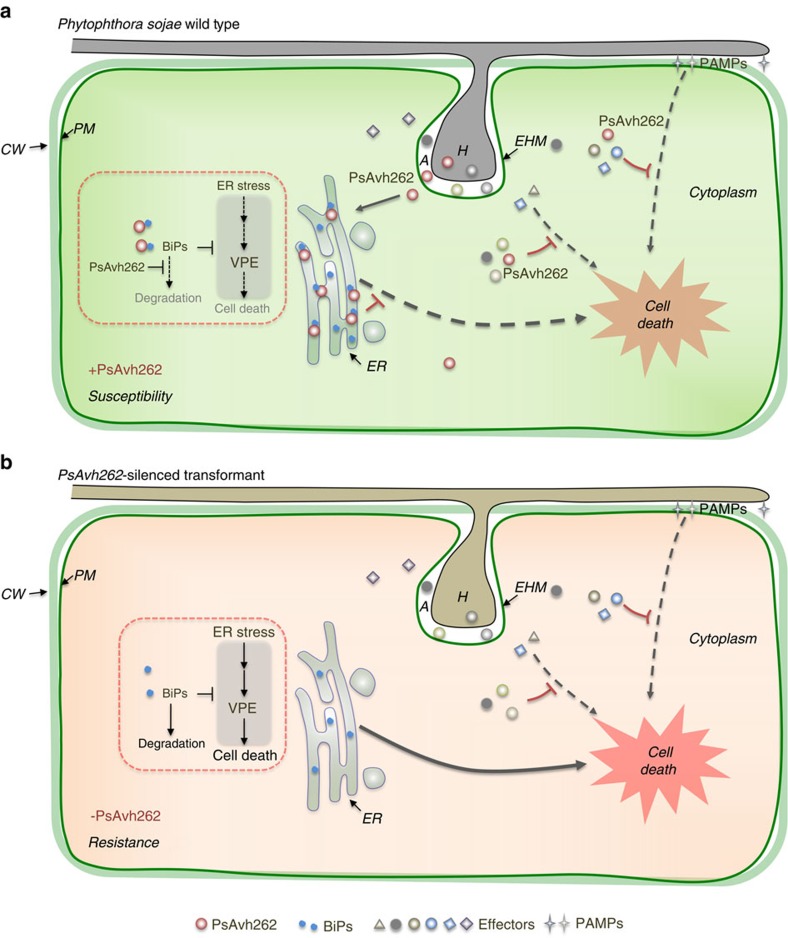
Figure 9. A schematic summary illustrating PsAvh262 suppression of ER stress-mediated immunity by stabilization of plant BiPs during infection.
During infection, P. sojae produces haustoria, through which effectors are secreted and translocated into host cells. In infected ‘haustoriated' cells, the host plasma membrane remains intact but is invaginated by the invading hyphae and becomes the extrahaustorial membrane (EHM). Phytophthora infection can activate the ER stress response in the host plants, which subsequently triggers cell death to block infection. (a) In the initial biotrophic phase, PsAvh262 associates and stabilizes host BiPs in the ER to attenuate the ER stress-triggered cell death. As such, PsAvh262 acts as an essential virulence factor to enhance P. sojae colonization and infection. Avh262 (along with many other RxLR effectors) can also suppress PAMP- and effector-triggered cell death, but it is unknown if this activity of Avh262 is mediated by the BiP interaction. (b) In the absence of PsAvh262, P. sojae is no longer able to attenuate the ER stress-induced cell death, which prevents infection. A, apoplast; CW, cell wall; EHM, extrahaustorial membrane; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; H, haustoria; PM, plasma membrane.