Fig. 1.
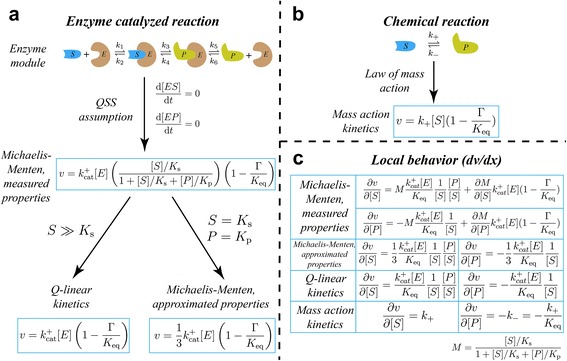
Comparison of rate laws and their resulting first derivatives. a Formulation of Michaelis-Menten kinetics with measured properties, Q-linear kinetics and Michaelis-Menten kinetics with approximated properties from the enzyme module with different layers of assumptions [42]. b Formulation of mass action kinetics based on the law of mass action for a pure chemical reaction. c First derivatives (reaction sensitivities) calculated from the four approximate rate laws. K s and K p are the Michaelis-Menten constants for the substrate and product. Γ is denoted as the mass-action ratio, which is the ratio of product concentrations over reactant concentrations in a steady state raised to the exponent of their stoichiometric coefficients. K eq is the equilibrium constant of the reaction. k cat + is the enzyme turnover rate constant. k +, as defined in MASS models, is the pseudo-elementary rate constant in the forward direction
