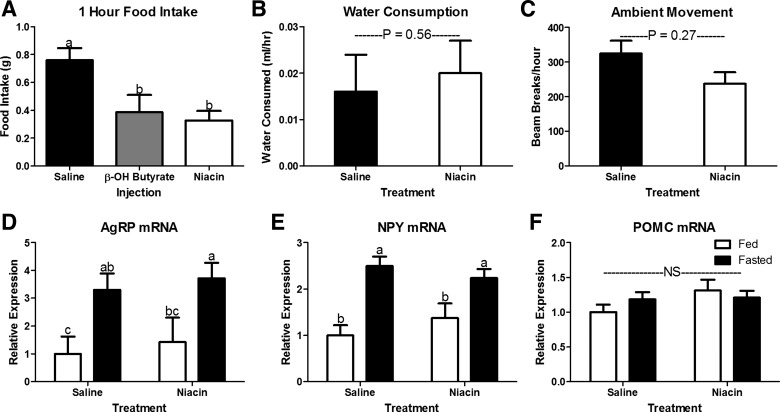
Fig. 2.
Phagic, behavioral, and neuroendocrine response to intraperitoneal β-OH butyrate and niacin injections. Intraperitoneal injection of β-OH butyrate (5.7 mmol/kg) and niacin (0.8 mmol/kg) decreased 1 h food intake in 16-h fasted mice (A; n = 8–13) but did not affect either water consumption (B; n = 4) or ambient movement (C; n = 4). Hypothalamic expression of mRNA encoding orexigenic [Agouti-related peptide (AgRP), D; neuropeptide Y (NPY), E] and anorexigenic [proopiomelanocortin (POMC), F] peptides in fed or fasted (16 h) mice injected with saline or niacin (0.8 mmol/kg) every 2 h for the last 8 h of the fast. NS, no significant difference. a,bBars that do not share a common letter differ significantly (P < 0.05; n = 6 or 7).