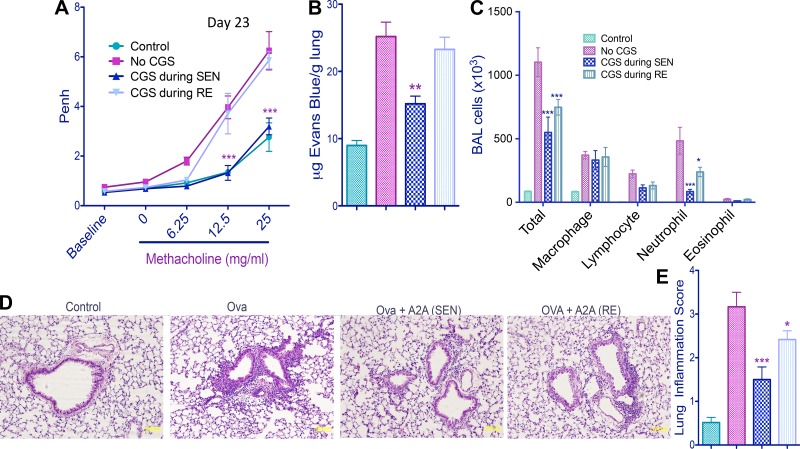
Fig. 4.
Effects of CGS treatment only during OVA-LPS sensitization (SEN) or only during OVA rechallenge (RE) on airway responsiveness to methacholine and lung inflammation. Control mice were not exposed to OVA or LPS. Other mice were challenged with OVA and LPS (see Fig. 1). Data were collected from C57BL/6J mice (n = 6) on day 23. A: dose-dependent changes in enhanced pause (Penh) in response to methacholine. ***P < 0.001 (by repeated-measures ANOVA and Bonferroni's multiple comparison test). B: pulmonary vascular leak assessed by accumulation of Evans blue dye uptake into the lung. C: accumulation of various cells into the BAL as determined after centrifugation (Cytospin) by morphology and staining with the PROTOCOL Hema 3 stain set. D: representative images of hematoxylin-eosin-stained lungs. “A2A” indicates A2AR activation by CGS-21680. Original magnification ×20. E: inflammation scores (see materials and methods) calculated by analysis of data from hematoxylin-eosin-stained mouse lungs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 vs. OVA/LPS (by 1-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparison tests).