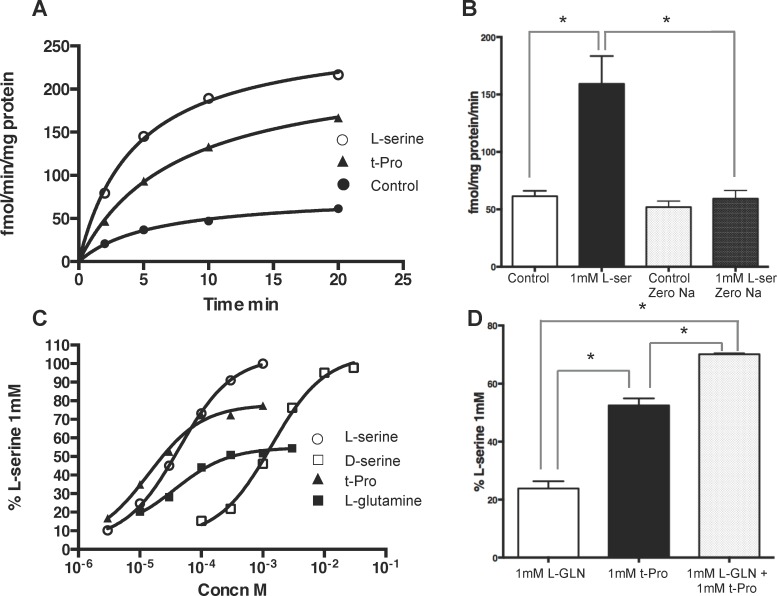
Fig 3. Exchange of [3H]L-serine by rat hippocampal astrocyte cultures.
After loading of cells with [3H]L-serine, amino acids were added to evoke exchange of [3H]L-serine into the supernatant as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Time course of exchange under control conditions (no added amino acid) and after addition of 1mM L-serine or 1mM t-Pro. Note the lower maximal effect of t-Pro. Data are from a single experiment that was repeated twice. (B) L-serine-evoked exchange is dependent on sodium; * p<0.01, t-test, n = 7 per group. (C) Concentration-response curves for exchange evoked by L- and D-serine, L-glutamine and t-Pro. Values are expressed as a percentage of the exchange caused by 1mM L-serine after subtraction of exchange in the absence of added amino acids. Curves were fitted using GraphPad Prism with a one-site fit. Data are from a single experiment that was repeated 3–14 times. EC50 and maximal effect values are shown in Table 4. (D) Effects of L-glutamine and t-Pro and their combination on exchange. Values are expressed as a percentage of the exchange caused by 1mM L-serine after subtraction of exchange in the absence of added amino acids; * p<0.01, t-test, n = 3 per group.