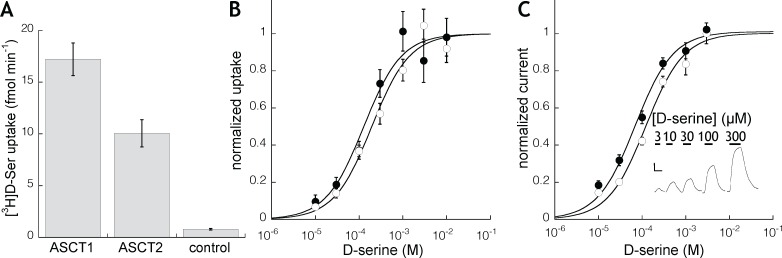
Fig 6. Uptake of D-serine by ASCT1 and ASCT2 expressed in Xenopus oocytes.
(A) Uptake of 100nM [3H]D-serine by Xenopus oocytes injected with human cRNA encoding SLC1A4 (ASCT1; n = 44), SLC1A5 (ASCT2; n = 45), or control, uninjected (n = 30). Uptake was significantly increased by mRNA injection (data from 4 batches of oocytes; bars represent mean ± SEM; p<0.001). (B) Concentration-dependence of [3H]D-serine uptake into oocytes injected with cRNA encoding SLC1A4 (filled circles) or SLC1A5 (open circles). Data points (mean ± SEM; n>6) fitted to the Michaelis-Menten function with KM values of 206 and 167 μM for SLC1A4 and SLC1A5, respectively. (C) Concentration-dependence of currents induced by D-serine in voltage-clamped oocytes injected with cRNA encoding SLC1A4/ASCT1 (closed circles; KM = 155+/-22 μM, n = 18) or SLC1A5/ASCT2 (open circles; KM = 107 ± 15 μM, n = 25). Inset shows representative recording in oocyte expressing SLC1A4; D-serine was superfused for durations and concentrations (μM) indicated by bars. Holding potential = -20 mV; scale bars 20 nA/60 sec. D-serine did not induce currents in uninjected oocytes (data not shown).