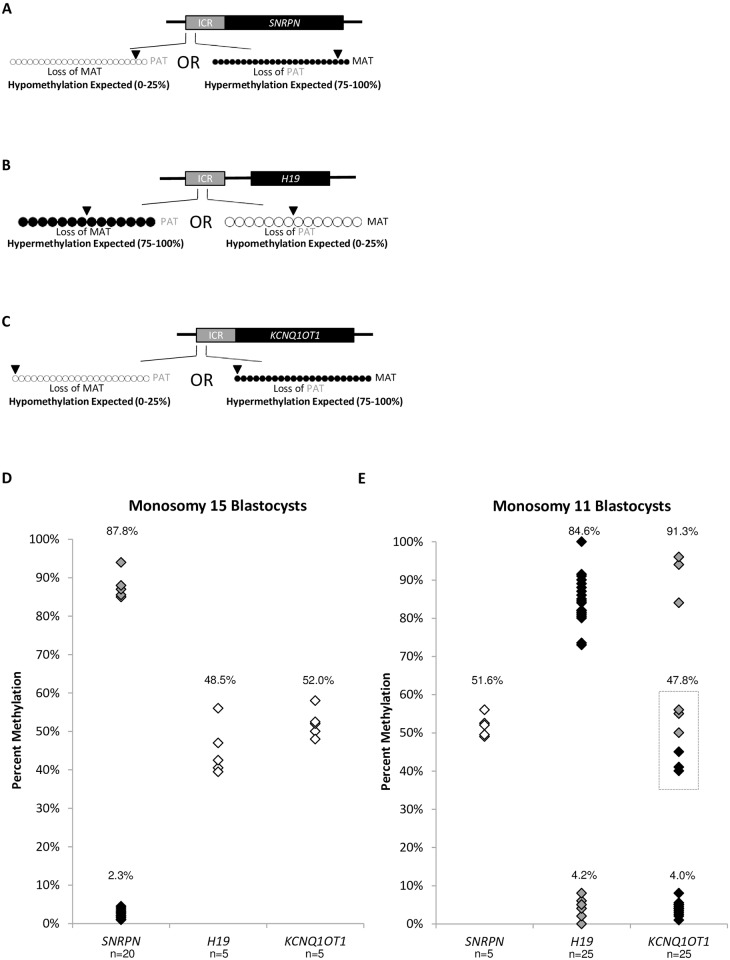
Fig 3. Imprinted DNA methylation profiles of monosomy blastocysts.
Black dots represent methylated CpGs, white dots represent unmethylated CpGs. The SNP location is indicated by an arrowhead. “MAT” represents the maternal oocyte-contributed allele; “PAT” represents the paternal sperm-contributed allele. A) Diagram of the SNRPN ICR amplified region analyzed in monosomy 15 blastocysts. Hypomethylation (0–25%) is expected with the presence of only the PAT allele. Hypermethylation (75–100%) is expected with the presence of only the MAT allele. B) Diagram of the H19 ICR amplified region analyzed in monosomy 11 blastocysts. Hypermethylation (75–100%) is expected with the presence of only the PAT allele. Hypomethylation (0–25%) is expected with the presence of only the MAT allele. C) Diagram of the KCNQ1OT1 ICR amplified region analyzed in monosomy 11 blastocysts. Hypomethylation (0–25%) is expected with the presence of only the PAT allele. Hypermethylation (75–100%) is expected with the presence of only the MAT allele. D) Summary chart of percent methylation in all monosomy 15 blastocysts at the SNRPN (n = 20), H19 (n = 5), and KCNQ1OT1 (n = 5) ICRs. Black diamonds represent blastocysts with presumable loss of a chromosome 15 from the oocyte, grey diamonds represent blastocysts with presumable loss of a chromosome 15 from the sperm. White diamonds represent the methylation percentage for the ICRs on diploid chromosome 11. Average percent methylation for each cohort is indicated. E) Summary chart of percent methylation in all monosomy 11 blastocysts at the SNRPN (n = 5), H19 (n = 25), and KCNQ1OT1 (n = 25) ICRs. Black diamonds represent blastocysts with presumable loss of a chromosome 11 from the oocyte, grey diamonds represent blastocysts with presumable loss of a chromosome 11 from the sperm. White diamonds represent the methylation percentage for the ICR on diploid chromosome 15. The grey dotted box highlights the six blastocysts with unexpected KCNQ1OT1 methylation profiles. Average percent methylation for each cohort is indicated. Methylation dot diagrams for individual monosomy blastocysts and diploid ICRs can be found in S3 and S4 Figs, and a summary can be found in S2 Table.