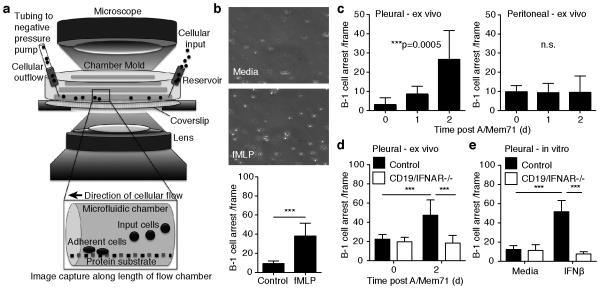
Figure 3. Infection-induced type I IFN signaling increases B-1 cell integrin-mediated adhesion.
(a) Schematic of a vascular mimetic microfluidic chamber used to observe adhesion of B-1 cells on cover slips coated with ICAM-1 and CXCL13 under shear flow. (b) Top 20X brightfield images of autoMACS purified B-1 cells in medium without (top) or with (bottom) 1uM fMLP. Bar chart shows mean B-1 cells arresting (± S. D.) (c) Adhesion assay showing mean numbers (± S. D.) of pleural and peritoneal cavity B-1 cell arrests by B-1 cells isolated from mice at indicated times of infection with A/Mem71. (d) As in c, with B-1 cells isolated from CD19/IFNAR−/− mice and littermate controls. (e) As in d, with cells stimulated in vitro with 200U IFNβ for 16 hours. Student’s t-test: n. s., not significant; *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001. Data representative of three (a) or two (b, c, d) separate experiments. In each experiment, purified B-1 cell samples for adhesion studies were pooled from n =12 mice per group.