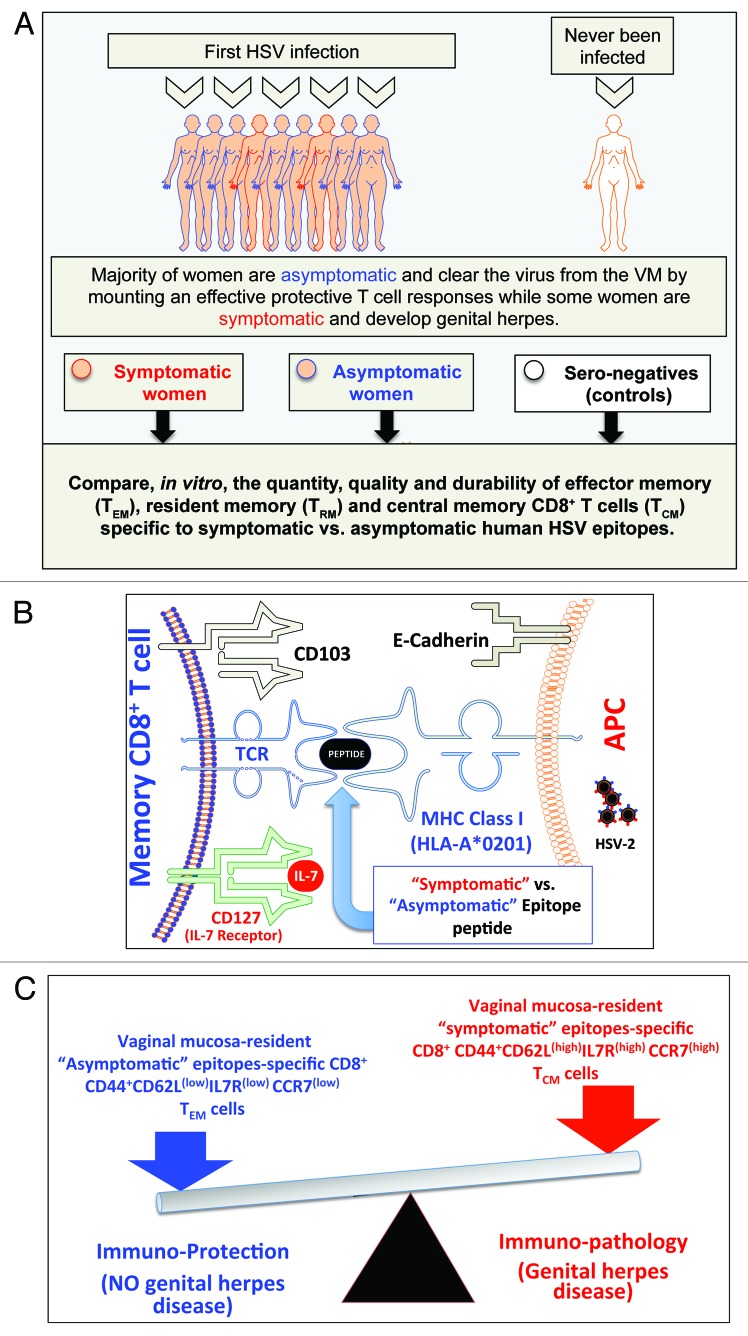
Figure 2. A proposed model of phenotypic and functional characteristics of HSV-specific CD8+ T cells in HSV-seropositive symptomatic vs. asymptomatic individuals: (A) Majority of women are asymptomatic and clear the virus from the VM by mounting a protective T cell responses while some women are symptomatic and develop genital herpes. Significant differences in the quantity, the quality and the durability of effector memory (TEM), tissue-resident memory (TRM) and central memory(TCM) CD8+ T cells specific to symptomatic vs. asymptomatic human HSV-2 epitopes are detected in symptomatic and asymptomatic women. (B) Potential interactions between an APC, presenting an asymptomatic vs. symptomatic epitope, (right) and a memory CD8+ T cell (left) occur in HSV-2 infected vaginal mucosa, and appear to be mediated by TCR/MHC, CD103/E-Cadherin, and CD127-IL7 pathways. (C) The balance between the asymptomatic vs. symptomatic epitopes will determine herpes protection vs. immunopathology.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.