Extended Data Figure 4. Comparison of catalytic and non-catalytic AlkD/3d3mA-DNA complexes.
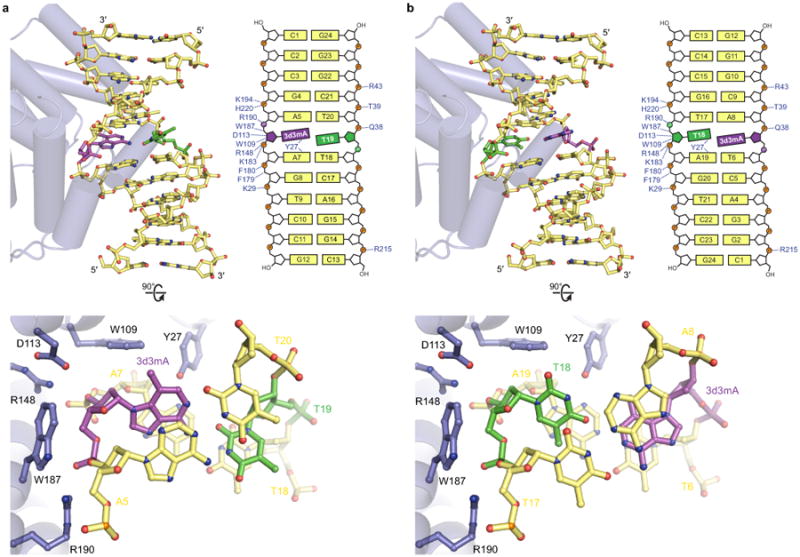
AlkD binds 3d3mA-DNA in two orientations that differ only in the position of the 3d3mA•T base pair about its dyad axis. Either 3d3mA (catalytic complex) or the opposing thymine (non-catalytic complex) resides against the protein surface. Both orientations use a common set of interactions that induce bending of the helical axis and widening of the minor groove, causing shearing of the 3d3mA•T base pair. In either complex, the nucleotide adjacent to the protein surface shows the same degree of displacement into the minor groove. The asymmetric position of the 3d3mA nucleotide in the duplex allows crystal packing interactions to select for a single orientation from a likely mixture of orientations in solution. Different DNA constructs were used to exploit these packing interactions and crystallize complexes in each binding orientation separately. Positive charge on the deoxyribose of 3mA would produce stronger electrostatic interactions with Trp109, Asp113, and Trp187 that would likely favor the catalytic binding orientation as well as a sheared conformation of a 3mA•T base pair. a, Catalytic orientation. The Watson-Crick conformer of the 3d3mA•T base pair was omitted for clarity. b, Non-catalytic orientation (PDB accession code 3JX7).
