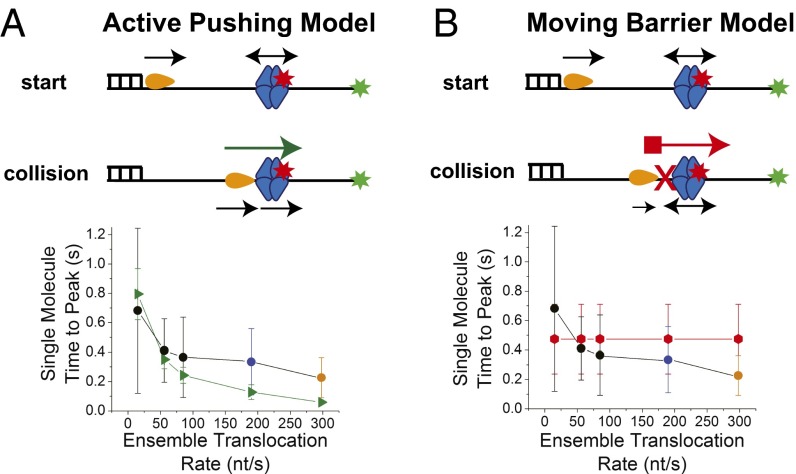
Fig. 4.
Translocases actively push SSB along ssDNA. (A) Active pushing model: The translocase initiates at the ds/ss DNA junction, whereas the SSB can bind randomly between the translocase and the DNA end-labeled with the Cy3 donor. On collision, the translocase can push the SSB along the ssDNA. Comparison of time-to-peak values as a function of translocation rate obtained from active pushing simulations (green triangles) with experimental single molecule median time-to-peak values: black circles, Pif1 pushing SSB at 5 mM, 500 μM, and 50 μM ATP; blue circle, UvrD pushing SSB at 5 mM ATP; orange circle, Rep pushing SSB at saturating 5 mM ATP. (B) Moving barrier model: On collision, the translocase cannot push the SSB, but presents a continuously advancing barrier only allowing SSB diffusion toward the Cy3 DNA end. Comparison of time-to-peak values as a function of translocation rate obtained from moving barrier simulations (red octagons) with experimental single molecule median time-to-peak values: black circles, Pif1 pushing SSB at 5 mM, 500 μM, and 50 μM ATP; blue circle, UvrD pushing SSB at 5 mM ATP; orange circle, Rep pushing SSB at saturating 5 mM ATP.