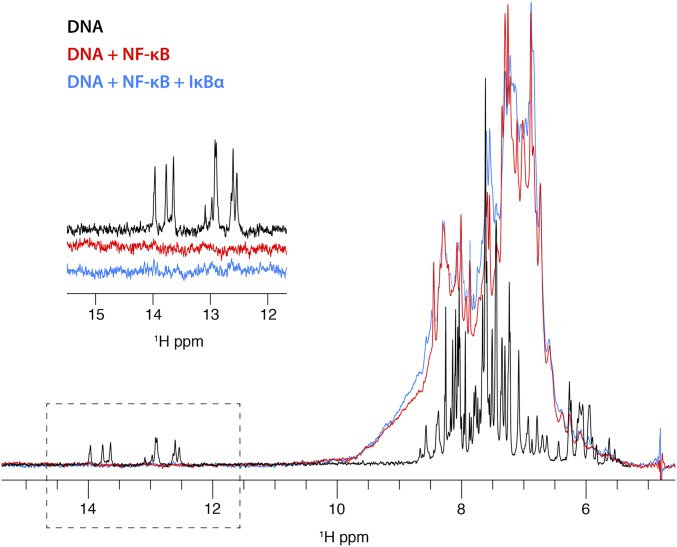
Fig. 3.
Portion of a 1D 1H spectrum of unlabeled duplex κB DNA (black) showing resonances at 12–14 ppm characteristic for hydrogen-bonded imino protons and resonances at 5–9 ppm characteristic of sugar and base protons of the DNA (the aliphatic portion of the spectrum, between 0 and 4 ppm has been omitted for clarity). Addition of perdeuterated NF-κB (red) gives a broadened spectrum representing both DNA and protein between 5 and 9 ppm, consistent with the incorporation of the DNA into an 83-kDa complex with NF-κB. The imino resonances of the DNA do not appear in this spectrum, likely due to broadening as a result of complex formation. The sharp resonances at 5.5–6 ppm in the DNA spectrum are also broadened. Further addition of IκBα to the NF-κB–DNA complex does not result in the reappearance of the imino resonances, indicating that the DNA remains part of the high molecular-weight complex instead of dissociating in the presence of IκBα.