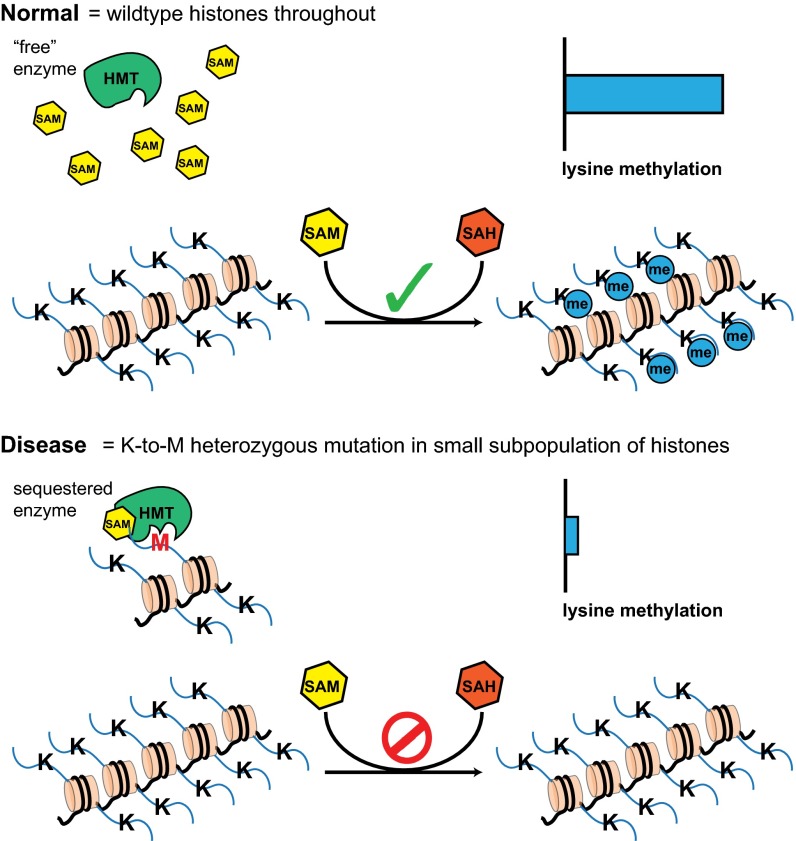
Fig. 5.
Model for sequestration and inhibition of histone lysine methyltransferases (HMTs) by oncohistones. Under normal conditions, HMTs catalyze the transfer of methyl groups from SAM to specific lysine residues on histones. In cells expressing K-to-M oncohistones, the high affinity of SAM-bound HMTs for oncohistone tails results in sequestration of the enzymes onto the mutant histone, whereas HMT cannot bind the K-to-M histone in the absence of SAM. The effective decrease of catalytically active HMTs results in a global reduction of histone methylation.